Polymorphism of the human alpha1 immunoglobulin gene 3' enhancer hs1,2 and its relation to gene expression
- PMID: 11380690
- PMCID: PMC1783220
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01217.x
Polymorphism of the human alpha1 immunoglobulin gene 3' enhancer hs1,2 and its relation to gene expression
Abstract
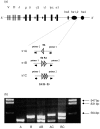
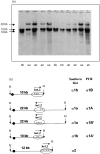
We studied the hs1,2 transcriptional enhancer identified downstream of the human alpha1 gene of the immunoglobulin H (IgH) locus, for which two different allelic configurations (a and b) were previously reported by Southern blotting. By using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method we amplified minisatellites within the hs1,2 core enhancer, with variable numbers of tandem repeats (VNTR) defining three 'PCR alleles' alpha1A, alpha1B and alpha1C (including one, two and three repeats, respectively). Five different alpha1 h1,2 genotypes were encountered in a population of 513 donors, representing 13.8, 34.5, 49.7, 1.3 and 0.6% for the AA, BB, AB, AC and BC genotypes, respectively. Luciferase assays showed that increasing the number of minisatellites increased the transcriptional strength of the alpha1 hs1,2 enhancer. Simultaneous determination of Southern blot alleles and VNTR alleles only showed a partial linkage between both types of polymorphism, altogether defining at least six different allelic forms of the 3'alpha1 region. In conclusion, the present study further demonstrates the genetic instability of the 3'alpha region, for which multiple alleles have been generated through inversions and internal deletions and/or duplications. This study also strengthens the hypothesis that the polymorphism at the IgH 3' regulatory region of the alpha1 gene could play a role in the outcome of diseases involving immunoglobulin secretion.
Figures


References
-
- CognÉ M, Lansford R, Bottaro A, Zhang J, Gorman J, Young F, Cheng HL, Alt FW. A class switch control region at the 3′ end of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Cell. 1994;77:737–47. - PubMed
-
- Khamlichi AA, Pinaud E, Decourt C, Chauveau C, CognÉ M. The 3′ IgH regulatory region: a complex structure in a search for a function. Adv Immunol. 2000;75:317–45. - PubMed
-
- Pinaud E, Aupetit C, Chauveau C, CognÉ M. Identification of a homologue of the Cα3′/hs3 enhancer and of an allelic variant of the 3′IgH/hs 1,2 enhancer downstream the human immunoglobulin α1 gene. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:2981–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

