Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural networks
- PMID: 11385503
- PMCID: PMC1282521
- DOI: 10.1038/89044
Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural networks
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to develop a method of classifying cancers to specific diagnostic categories based on their gene expression signatures using artificial neural networks (ANNs). We trained the ANNs using the small, round blue-cell tumors (SRBCTs) as a model. These cancers belong to four distinct diagnostic categories and often present diagnostic dilemmas in clinical practice. The ANNs correctly classified all samples and identified the genes most relevant to the classification. Expression of several of these genes has been reported in SRBCTs, but most have not been associated with these cancers. To test the ability of the trained ANN models to recognize SRBCTs, we analyzed additional blinded samples that were not previously used for the training procedure, and correctly classified them in all cases. This study demonstrates the potential applications of these methods for tumor diagnosis and the identification of candidate targets for therapy.
Figures
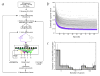

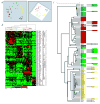
Comment in
-
Microarrays--the 21st century divining rod?Nat Med. 2001 Jun;7(6):658-9. doi: 10.1038/89022. Nat Med. 2001. PMID: 11385496 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Chips help diagnosis of childhood cancers.Trends Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;11(8):323. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(01)02078-5. Trends Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11489636 No abstract available.
-
Tumor classification by combining PNN classifier ensemble with neighborhood rough set based gene reduction.Comput Biol Med. 2010 Feb;40(2):179-89. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2009.11.014. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Comput Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20044083
-
PCA disjoint models for multiclass cancer analysis using gene expression data.Bioinformatics. 2003 Mar 22;19(5):571-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg051. Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12651714
-
[Cytopathology of malignant blastematous tumors].Ann Pathol. 2004 Dec;24(6):568-73. doi: 10.1016/s0242-6498(04)94019-9. Ann Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15785403 Review. French.
-
Rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing Sarcoma, and Other Round Cell Sarcomas.J Clin Oncol. 2018 Jan 10;36(2):168-179. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.7402. Epub 2017 Dec 8. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29220292 Review.
Cited by
-
Bicoid signal extraction with a selection of parametric and nonparametric signal processing techniques.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015 Jun;13(3):183-91. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2015.02.006. Epub 2015 Jul 18. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26197438 Free PMC article.
-
Ensemble methods of rank-based trees for single sample classification with gene expression profiles.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 7;22(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04940-2. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38321494 Free PMC article.
-
FGFR4 blockade exerts distinct antitumorigenic effects in human embryonal versus alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 15;18(14):3780-90. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3063. Epub 2012 May 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22648271 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of tumor samples from expression data using decision trunks.Cancer Inform. 2013;12:53-66. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S10356. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Cancer Inform. 2013. PMID: 23467331 Free PMC article.
-
Complex temporal changes in TGFβ oncogenic signaling drive thyroid carcinogenesis in a mouse model.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Oct;34(10):2389-400. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt175. Epub 2013 May 22. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23698635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pizzo, P.A. Principles and practice of pediatric oncology (Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, 1997).
-
- Triche TJ, Askin FB. Neuroblastoma and the differential diagnosis of small-, round-, blue- cell tumors. Hum Pathol. 1983;14:569–595. - PubMed
-
- McManus AP, Gusterson BA, Pinkerton CR, Shipley JM. The molecular pathology of small round-cell tumours—relevance to diagnosis, prognosis, and classification. J Pathol. 1996;178:116–121. - PubMed
-
- Khan J, et al. Gene expression profiling of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma with cDNA microarrays. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5009–5013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

