The Rab GTPase family
- PMID: 11387043
- PMCID: PMC138937
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2001-2-5-reviews3007
The Rab GTPase family
Abstract
The Rab family is part of the Ras superfamily of small GTPases. There are at least 60 Rab genes in the human genome, and a number of Rab GTPases are conserved from yeast to humans. The different Rab GTPases are localized to the cytosolic face of specific intracellular membranes, where they function as regulators of distinct steps in membrane traffic pathways. In the GTP-bound form, the Rab GTPases recruit specific sets of effector proteins onto membranes. Through their effectors, Rab GTPases regulate vesicle formation, actin- and tubulin-dependent vesicle movement, and membrane fusion.
Figures
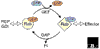


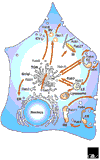
References
-
- Touchot N, Chardin P, Tavitian A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84:8210–8214. Describes the identification of the first mammalian Rab GTPases, and the term 'Rab' is introduced. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stenmark H, Parton RG, Steele-Mortimer O, Lütcke A, Gruenberg J, Zerial M. Inhibition of rab5 GTPase activity stimulates membrane fusion in endocytosis. EMBO J. 1994;13:1287–1296. Shows that a GTPase-deficient mutant of Rab5 stimulates endocytic membrane fusion, whereas a GDP-bound mutant has the opposite effect. Identifies the GTP-bound form as the 'active' one. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bock JB, Matern HT, Peden AA, Scheller RH. A genomic perspective on membrane compartment organization. Nature. 2001;409:839–841. doi: 10.1038/35057024. Using information from expressed sequence tags and the recently published genome sequences, this paper describes a bioinformatic analysis of several protein families involved in membrane traffic, including Rab GTPases. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC. The mammalian Rab family of small GTPases: definition of family and subfamily sequence motifs suggests a mechanism for functional specificity in the Ras superfamily. J Mol Biol. 2000;301:1077–1087. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4010. This outstanding report contains extensive sequence comparisons within the Rab family and analysis of the results along with the information available from crystallography studies. The authors define sequence motifs that can be used to identify proteins belonging to the Rab family, and further, to specify subfamilies. A model is presented in which an effector, upon binding to a Rab, recognizes both Rab family-specific (switch) motifs to discriminate between the nucleotide-bound states, and simultaneously subfamily-specific regions that confer specificity on the interaction. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

