Heme mediates derepression of Maf recognition element through direct binding to transcription repressor Bach1
- PMID: 11387216
- PMCID: PMC125477
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.11.2835
Heme mediates derepression of Maf recognition element through direct binding to transcription repressor Bach1
Abstract
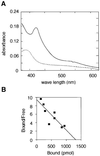
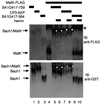
Heme controls expression of genes involved in the synthesis of globins and heme. The mammalian transcription factor Bach1 functions as a repressor of the Maf recognition element (MARE) by forming antagonizing hetero-oligomers with the small Maf family proteins. We show here that heme binds specifically to Bach1 and regulates its DNA-binding activity. Deletion studies demonstrated that a heme-binding region of Bach1 is confined within its C-terminal region that possesses four dipeptide cysteine-proline (CP) motifs. Mutations in all of the CP motifs of Bach1 abolished its interaction with heme. The DNA-binding activity of Bach1 as a MafK hetero-oligomer was markedly inhibited by heme in gel mobility shift assays. The repressor activity of Bach1 was lost upon addition of hemin in transfected cells. These results suggest that increased levels of heme inactivate the repressor Bach1, resulting in induction of a host of genes with MARES:
Figures






References
-
- Alam J., Stewart,D., Touchard,C., Boinapally,S., Choi,A.M. and Cook,J.L. (1999) Nrf2, a Cap’n’collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 26071–26078. - PubMed
-
- Blouin J.L., Duriaux Sail,G., Guipponi,M., Rossier,C., Pappasavas,M.P. and Antonarakis,S.E. (1998) Isolation of the human BACH1 transcription regulator gene, which maps to chromosome 21q22.1. Hum. Genet., 102, 282–288. - PubMed
-
- Chen J.J., Pal,J.K., Petryshyn,R., Kuo,I., Yang,J.M., Throop,M.S., Gehrke,L. and London,I.M. (1991a) Amino acid microsequencing of internal tryptic peptides of heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2α subunit kinase: homology to protein kinases. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 88, 315–319. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen J.J., Throop,M.S., Gehrke,L., Kuo,I., Pal,J.K., Brodsky,M. and London,I.M. (1991b) Cloning of the cDNA of the heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eIF-2α) kinase of rabbit reticulocytes: homology to yeast GCN2 protein kinase and human double-stranded-RNA-dependent eIF-2α kinase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 88, 7729–7733. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Creusot F., Verdiere,J., Gaisne,M. and Slonimski,P.P. (1989) CYP1 (HAP1) regulator of oxygen-dependent gene expression in yeast. I. Overall organization of the protein sequence displays several novel structural domains. J. Mol. Biol., 204, 263–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

