Evidence for the role of alveolar epithelial gp60 in active transalveolar albumin transport in the rat lung
- PMID: 11389211
- PMCID: PMC2278625
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0547a.x
Evidence for the role of alveolar epithelial gp60 in active transalveolar albumin transport in the rat lung
Abstract
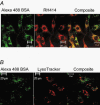
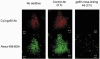
1. Transcytosis of albumin, involving the 60 kDa albumin-binding glycoprotein, gp60, was studied in cultured type II alveolar epithelial cells obtained from rat lungs. 2. Type II cells internalized the interfacial fluorescent dye RH 414, which marks for plasmalemma vesicles. Fluorescent forms of albumin and anti-gp60 antibody colocalized in the same plasmalemma vesicles. 3. Antibody (100 microg ml(-1)) cross-linking of gp60 for brief periods (15 min) markedly stimulated vesicular uptake of fluorescently tagged albumin. The caveolar disrupting agent, filipin (10 nM), abolished the stimulated internalization of albumin. 4. The vast majority of plasmalemmal vesicles carrying albumin also immunostained for caveolin-1; however, lysosomes did not stain for caveolin-1. Filipin depleted the epithelial cells of the caveolin-1-positive, albumin-transporting plasmalemma vesicles. 5. Prolonged (> 1 h) stimulation of type II cells with cross-linking anti-gp60 antibody produced loss of cell-surface gp60 and abolished endocytic albumin uptake. 6. Transalveolar transport of albumin was also studied in the isogravimetric rat lung preparation perfused at 37 degrees C. (125)I-labelled albumin was instilled into distal airspaces of lungs, and the resulting (125)I-labelled albumin efflux into the vascular perfusate was determined. 7. Unlabelled albumin (studied over a range of 0-10 g (100 instilled ml)(-1)) inhibited 40 % of the transport of labelled albumin ((5.7 +/- 0.4) x 10(5) counts (instilled ml)(-1)) with an IC(50) value of 0.34 g (100 ml)(-1). 8. Filipin blocked the displacement-sensitive component of (125)I-labelled albumin transport, but had no effect on the transport of the paracellular tracer (3)[H]mannitol. 9. Displacement-sensitive (125)I-labelled albumin transport had a significantly greater Q(10) (27-37 degrees C) than the non-displaceable component. 10. Cross-linking of gp60 by antibody instillation stimulated only the displacement-sensitive (125)I-labelled albumin transalveolar transport in intact rat lungs. 11. To estimate the transport capacity of the displacement-sensitive system, the percentage of instilled (125)I-labelled albumin counts remaining in lung tissue was compared in lungs treated with instillates containing either 0.05 g (100 ml)(-1) unlabelled albumin or 5 g (100 ml)(-1) unlabelled albumin. Approximately 25 % of instilled (125)I-labelled albumin was cleared from the lung preparations per hour by the displacement-sensitive transport pathway. This component was blocked by filipin.
Figures




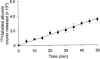


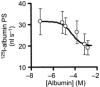
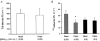
 ) but not elevated (5 g (100 ml)−1, ▪) unlabelled albumin concentration. Note that filipin affected only displaceable 125I-labelled albumin transport. Error bars, 1
) but not elevated (5 g (100 ml)−1, ▪) unlabelled albumin concentration. Note that filipin affected only displaceable 125I-labelled albumin transport. Error bars, 1 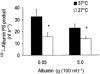

Similar articles
-
Endothelial cell-surface gp60 activates vesicle formation and trafficking via G(i)-coupled Src kinase signaling pathway.J Cell Biol. 2000 Sep 4;150(5):1057-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.1057. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10973995 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin uptake and transcytosis in endothelial cells in vivo induced by albumin-binding protein.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001 Dec;281(6):L1512-22. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.281.6.L1512. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11704548
-
Gp60 activation mediates albumin transcytosis in endothelial cells by tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway.J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 10;272(41):25968-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.41.25968. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9325331
-
Receptor-mediated endocytosis of macromolecules and strategy to enhance their transport in alveolar epithelial cells.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 May;12(5):813-25. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2015.992778. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25496474 Review.
-
Transendothelial transport: the vesicle controversy.J Vasc Res. 2002 Sep-Oct;39(5):375-90. doi: 10.1159/000064521. J Vasc Res. 2002. PMID: 12297701 Review.
Cited by
-
Src-dependent phosphorylation of caveolin-1 Tyr-14 promotes swelling and release of caveolae.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jul 1;27(13):2090-106. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-11-0756. Epub 2016 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27170175 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Delivery of Biological Drugs.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Oct 26;12(11):1025. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111025. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33114726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PepFect14 Signaling and Transfection.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2383:229-246. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1752-6_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34766293
-
Mitigation of chlorine-induced lung injury by low-molecular-weight antioxidants.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Nov;295(5):L733-43. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90240.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18708632 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of albumin uptake in rat alveolar type II and type I-like epithelial cells in primary culture.Pharm Res. 2008 Apr;25(4):913-22. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9426-x. Epub 2007 Sep 11. Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 17851738
References
-
- Berthiaume Y, Albertine KH, Grady M, Fick G, Matthay MA. Protein clearance from the airspaces and lungs of unanesthetized sheep over 144 h. Journal of Applied Physiology. 1989;67:1887–1897. - PubMed
-
- Bittman R. Sterol-polyene antibiotic complexation: probe of membrane structure. Lipids. 1978;13:686–691. - PubMed
-
- Bocci V. Efficient labeling of serum proteins with I-131 using chloramine T. International Journal of Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 1964;15:449–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

