Krüppel-like factor 4 (gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor) inhibits cell proliferation by blocking G1/S progression of the cell cycle
- PMID: 11390382
- PMCID: PMC2330258
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M101194200
Krüppel-like factor 4 (gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor) inhibits cell proliferation by blocking G1/S progression of the cell cycle
Abstract
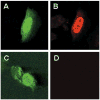
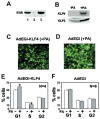
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is an epithelial cell-enriched, zinc finger-containing transcription factor, the expression of which is associated with growth arrest. Previous studies show that constitutive expression of KLF4 inhibits DNA synthesis but the manner by which KLF4 exerts this effect is unclear. In the present study, we developed a system in which expression of KLF4 is controlled by a promoter that is induced upon treatment of cells containing the receptors for the insect hormone, ecdysone, with ponasterone A, an ecdysone analogue. The rate of proliferation of a stably transfected colon cancer cell line, RKO, was significantly decreased following addition of ponasterone A when compared with untreated cells. Flow cytometric analyses indicated that the inducible expression of KLF4 caused a block in the G(1)/S phase of the cell cycle. A similar block was observed when ecdysone receptor-containing RKO cells were infected with a replication-defective recombinant adenovirus containing an inducible KLF4 and treated with ponasterone A. Results of these studies provide evidence that the inhibitory effect of KLF4 on cell proliferation is mainly exerted at the G(1)/S boundary of the cell cycle.
Figures



References
-
- Garrett-Sinha LA, Eberspaecher H, Seldin MF, de Crombrugghe B. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:31384–31390. - PubMed
-
- Schuh R, Aicher W, Gual U, Cote S, Preiss A, Maier D, Seifert E, Nauber U, Shroder C, Kemler R, Jackle H. Cell. 1986;47:1025–1032. - PubMed
-
- Turner J, Crossley M. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:236–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

