Human cd25(+)cd4(+) t regulatory cells suppress naive and memory T cell proliferation and can be expanded in vitro without loss of function
- PMID: 11390436
- PMCID: PMC2193376
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.11.1295
Human cd25(+)cd4(+) t regulatory cells suppress naive and memory T cell proliferation and can be expanded in vitro without loss of function
Abstract
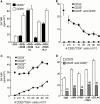
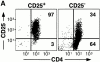
Active suppression by T regulatory (Tr) cells plays an important role in the downregulation of T cell responses to foreign and self-antigens. Mouse CD4(+) Tr cells that express CD25 possess remarkable suppressive activity in vitro and in autoimmune disease models in vivo. Thus far, the existence of a similar subset of CD25(+)CD4(+) Tr cells in humans has not been reported. Here we show that human CD25(+)CD4(+) Tr cells isolated from peripheral blood failed to proliferate and displayed reduced expression of CD40 ligand (CD40L), in response to T cell receptor-mediated polyclonal activation, but strongly upregulated cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen (CTLA)-4. Human CD25(+)CD4(+) Tr cells also did not proliferate in response to allogeneic antigen-presenting cells, but they produced interleukin (IL)-10, transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta, low levels of interferon (IFN)-gamma, and no IL-4 or IL-2. Importantly, CD25(+)CD4(+) Tr cells strongly inhibited the proliferative responses of both naive and memory CD4(+) T cells to alloantigens, but neither IL-10, TGF-beta, nor CTLA-4 seemed to be directly required for their suppressive effects. CD25(+)CD4(+) Tr cells could be expanded in vitro in the presence of IL-2 and allogeneic feeder cells and maintained their suppressive capacities. These findings that CD25(+)CD4(+) Tr cells with immunosuppressive effects can be isolated from peripheral blood and expanded in vitro without loss of function represent a major advance towards the therapeutic use of these cells in T cell-mediated diseases.
Figures






References
-
- Roncarolo M.G., Levings M.K. The role of different subsets of T regulatory cells in controlling autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2000;12:676–683. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cellskey controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell. 2000;101:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Shevach E.M. Regulatory T cells in autoimmmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000;18:423–449. - PubMed
-
- Cottrez F., Hurst S.D., Coffman R.L., Groux H. T regulatory cells 1 inhibit a Th2-specific response in vivo. J. Immunol. 2000;165:4848–4853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

