CD4(+)CD25(+) immune regulatory cells are required for induction of tolerance to alloantigen via costimulatory blockade
- PMID: 11390438
- PMCID: PMC2193378
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.11.1311
CD4(+)CD25(+) immune regulatory cells are required for induction of tolerance to alloantigen via costimulatory blockade
Abstract
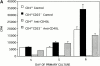
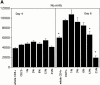
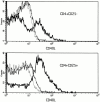
Immune regulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) cells play a vital role in the induction and maintenance of self-tolerance and are essential for T cell homeostasis and the prevention of autoimmunity. Induction of tolerance to allogeneic donor grafts is a clinically desirable goal in bone marrow and solid organ transplantation. To determine whether CD4(+)CD25(+) cells regulate T cell responses to alloantigen and are critical for tolerance induction, murine CD4(+) T cells were tolerized to alloantigen via ex vivo CD40 ligand (CD40L)/CD40 or CD28/cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4/B7 blockade resulting in secondary mixed leukocyte reaction hyporesponsiveness and tolerance to alloantigen in vivo. CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells were found to be potent regulators of alloresponses. Depletion of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells from the CD4(+) responder population completely abrogated ex vivo tolerance induction to alloantigen as measured by intact responses to alloantigen restimulation in vitro and in vivo. Addback of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells to CD4(+)CD25(-) cultures restored tolerance induction. These data are the first to indicate that CD4(+)CD25(+) cells are essential for the induction of tolerance to alloantigen and have important implications for tolerance-inducing strategies targeted at T cell costimulatory pathways.
Figures







References
-
- Sakaguchi S., Sakaguchi N., Asano M., Itoh M., Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor α-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J. Immunol. 1995;155:1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Suri-Payer E., Kehn P.J., Cheever A.W., Shevach E.M. Pathogenesis of post-thymectomy autoimmune gastritis. Identification of anti-H/K adenosine triphosphatase-reactive T cells. J. Immunol. 1996;157:1799–1805. - PubMed
-
- Bonomo A., Kehn P.J., Payer E., Rizzo L., Cheever A.W., Shevach E.M. Pathogenesis of post-thymectomy autoimmunity. Role of syngeneic MLR-reactive T cells. J. Immunol. 1995;154:6602–6611. - PubMed
-
- Willerford D.M., Chen J., Ferry J.A., Davidson L., Ma A., Alt F.W. Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain regulates the size and content of the peripheral lymphoid compartment. Immunity. 1995;3:521–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

