Adenylate kinase phosphotransfer communicates cellular energetic signals to ATP-sensitive potassium channels
- PMID: 11390963
- PMCID: PMC34718
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.121038198
Adenylate kinase phosphotransfer communicates cellular energetic signals to ATP-sensitive potassium channels
Abstract
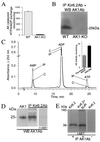
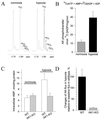
Transduction of energetic signals into membrane electrical events governs vital cellular functions, ranging from hormone secretion and cytoprotection to appetite control and hair growth. Central to the regulation of such diverse cellular processes are the metabolism sensing ATP-sensitive K+ (K(ATP)) channels. However, the mechanism that communicates metabolic signals and integrates cellular energetics with K(ATP) channel-dependent membrane excitability remains elusive. Here, we identify that the response of K(ATP) channels to metabolic challenge is regulated by adenylate kinase phosphotransfer. Adenylate kinase associates with the K(ATP) channel complex, anchoring cellular phosphotransfer networks and facilitating delivery of mitochondrial signals to the membrane environment. Deletion of the adenylate kinase gene compromised nucleotide exchange at the channel site and impeded communication between mitochondria and K(ATP) channels, rendering cellular metabolic sensing defective. Assigning a signal processing role to adenylate kinase identifies a phosphorelay mechanism essential for efficient coupling of cellular energetics with K(ATP) channels and associated functions.
Figures
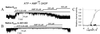
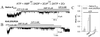


References
-
- Weiss J N, Lamp S T. Science. 1987;238:67–69. - PubMed
-
- O'Rourke B, Ramza B M, Marban E. Science. 1994;265:962–966. - PubMed
-
- Noma A. Nature (London) 1983;305:147–148. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft F M, Harrison D E, Ashcroft S J. Nature (London) 1984;312:446–448. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Clement J P, Namba N, Inazawa J, Gonzalez G, Aguilar-Bryan L, Seino S, Bryan J. Science. 1995;270:1166–1170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

