Model of cellular and network mechanisms for odor-evoked temporal patterning in the locust antennal lobe
- PMID: 11395015
- PMCID: PMC2907737
- DOI: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00286-0
Model of cellular and network mechanisms for odor-evoked temporal patterning in the locust antennal lobe
Abstract
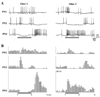
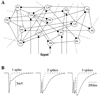
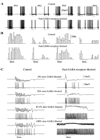
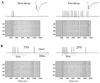
Locust antennal lobe (AL) projection neurons (PNs) respond to olfactory stimuli with sequences of depolarizing and hyperpolarizing epochs, each lasting hundreds of milliseconds. A computer simulation of an AL network was used to test the hypothesis that slow inhibitory connections between local neurons (LNs) and PNs are responsible for temporal patterning. Activation of slow inhibitory receptors on PNs by the same GABAergic synapses that underlie fast oscillatory synchronization of PNs was sufficient to shape slow response modulations. This slow stimulus- and neuron-specific patterning of AL activity was resistant to blockade of fast inhibition. Fast and slow inhibitory mechanisms at synapses between LNs and PNs can thus form dynamical PN assemblies whose elements synchronize transiently and oscillate collectively, as observed not only in the locust AL, but also in the vertebrate olfactory bulb.
Figures


Comment in
-
Smelling well with a code in the nodes.Neuron. 2001 May;30(2):307-9. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00310-5. Neuron. 2001. PMID: 11394993 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bazhenov M, Timofeev I, Steriade M, Sejnowski TJ. Cellular and network models for intrathalamic augmenting responses during 10 Hz stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 1998;79:2730–2748. - PubMed
-
- Burrows M, Boeckh J, Esslen J. Physiological and morphological properties of interneurons in the deutocerebrum of male cockroaches which respond to female pheromone. J. Comp. Physiol. A. 1982;145:447–457.
-
- Chaput M, Holley A. Single unit responses of olfactory bulb neurons to odor presentation in awake rabbits. J. Physiol. 1980;76:551–558. - PubMed
-
- Christensen T, Hildebrand J. Male-specific, sex phero-mone-selective projection neurons in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta. J. Comp. Physiol. A. 1987;160:553–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

