p53 cellular localization and function in neuroblastoma: evidence for defective G(1) arrest despite WAF1 induction in MYCN-amplified cells
- PMID: 11395384
- PMCID: PMC1892004
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64678-0
p53 cellular localization and function in neuroblastoma: evidence for defective G(1) arrest despite WAF1 induction in MYCN-amplified cells
Abstract
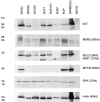
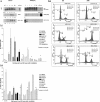
This study investigated the hypothesis that p53 accumulation in neuroblastoma, in the absence of mutation, is associated with functional inactivation, which interferes with downstream mediators of p53 function. To test this hypothesis, p53 expression, location, and functional integrity was examined in neuroblastoma by irradiating 6 neuroblastoma cell lines and studying the effects on p53 transcriptional function, cell cycle arrest, and induction of apoptosis, together with the transcriptional function of p53 after irradiation in three ex vivo primary, untreated neuroblastoma tumors. p53 sequencing showed five neuroblastoma cell lines, two of which were MYCN-amplified, and that all of the tumors were wild-type for p53. p53 was found to be predominantly nuclear before and after irradiation and to up-regulate the p53 responsive genes WAF1 and MDM2 in wild-type p53 cell lines and a poorly-differentiated neuroblastoma, but not a differentiating neuroblastoma or the ganglioneuroblastoma part of a nodular ganglioneuroblastoma in short term culture. This suggests intact p53 transcriptional activity in proliferating neuroblastoma. Irradiation of wild-type p53 neuroblastoma cell lines led to G(1) cell cycle arrest in cell lines without MYCN amplification, but not in those with MYCN amplification, despite induction of WAF1. This suggests MYCN amplification may alter downstream mediators of p53 function in neuroblastoma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of MYCN in the failure of MYCN amplified neuroblastoma cell lines to G1 arrest after DNA damage.Cell Cycle. 2006 Nov;5(22):2639-47. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.22.3443. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 17172827
-
Wild-type p53 can induce p21 and apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells but the DNA damage-induced G1 checkpoint function is attenuated.Clin Cancer Res. 1999 Dec;5(12):4199-207. Clin Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10632361
-
Relationships between G1 arrest and stability of the p53 and p21Cip1/Waf1 proteins following gamma-irradiation of human lymphoma cells.Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 1;55(11):2387-93. Cancer Res. 1995. PMID: 7757991
-
The p53 pathway and its inactivation in neuroblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2003 Jul 18;197(1-2):93-8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(03)00088-0. Cancer Lett. 2003. PMID: 12880966 Review.
-
MDM2 as MYCN transcriptional target: implications for neuroblastoma pathogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2005 Oct 18;228(1-2):21-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.01.050. Cancer Lett. 2005. PMID: 15927364 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of Cupressus sempervirens extract against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats.Interdiscip Toxicol. 2015 Mar;8(1):25-34. doi: 10.1515/intox-2015-0006. Interdiscip Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 27486357 Free PMC article.
-
TDP-43 regulates the microprocessor complex activity during in vitro neuronal differentiation.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Dec;48(3):952-63. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8564-x. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 24113842
-
Shikimic acid recovers diarrhea and its complications in SD rats fed lactose diet to induce diarrhea.Lab Anim Res. 2023 Nov 10;39(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s42826-023-00179-y. Lab Anim Res. 2023. PMID: 37950334 Free PMC article.
-
TP53 mutant MDM2-amplified cell lines selected for resistance to MDM2-p53 binding antagonists retain sensitivity to ionizing radiation.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):46203-46218. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10073. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27323823 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting nucleocytoplasmic transport in cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2014 Jan 15;5(1):11-28. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1457. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24429466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pearson ADJ, Philip T: Prognosis of low-risk and high-risk neuroblastoma. Brodeur GM Sawada T Tsuchida Y Voute PA eds. Neuroblastoma. 2000, :pp 551-570 Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Amsterdam
-
- Tweddle DA, Pinkerton CR, Lewis IJ, Ellershaw C, Cole M, Pearson ADJ: OPEC/OJEC for stage 4 neuroblastoma over 1 year of age. Med Pediatr Oncol 2001, 36:239-242 - PubMed
-
- Levine A: p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88:323-331 - PubMed
-
- Kirsch D, Kastan M: Tumour suppressor p53: implications for tumor development and prognosis. J Clin Oncol 1998, 16:3158-3168 - PubMed
-
- Vogan K, Bernstein M, Leclerc J-M, Brisson L, Brossard J, Brodeur G, Pelletier J, Gros P: Absence of p53 gene mutations in primary neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 1993, 53:5269-5273 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

