Quantitative assessment of the rat intrahepatic biliary system by three-dimensional reconstruction
- PMID: 11395385
- PMCID: PMC1891969
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64679-2
Quantitative assessment of the rat intrahepatic biliary system by three-dimensional reconstruction
Abstract
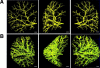
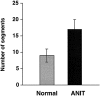
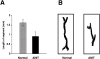
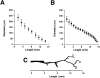
The anatomical details of the biliary tree architecture of normal rats and rats in whom selective proliferation was induced by feeding alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) were reconstructed in three dimension using a microscopic-computed tomography scanner. The intrahepatic biliary tree was filled with a silicone polymer through the common bile duct and each liver lobe embedded in Bioplastic; specimens were then scanned by a microscopic-computed tomography scanner and modified Feldkamp cone beam backprojection algorithm applied to generate three-dimensional images. Quantitative analysis of bile duct geometry was performed using a customized software program. The diameter of the bile duct segments of normal and ANIT-fed rats progressively decreased with increasing length of the biliary tree. Diameter of bile ducts from ANIT-fed rats (range, 21 to 264 microm) was similar to that of normal rats (22 to 279 microm). In contrast, the number of bile duct segments along the major branch reproducibly doubled, the length of the bile duct segments decreased twofold, and the length of the biliary tree remained unchanged after ANIT feeding. Moreover, the total volume of the biliary tree of ANIT-fed rats was significantly greater (855 microl) than in normal rats (47 microl). Compared with normal rats, the total surface area of the biliary tree increased 26 times after ANIT-induced bile duct proliferation. Taken together, these observations quantitate the anatomical remodeling after selective cholangiocyte proliferation and strongly suggest that the proliferative process involves sprouting of new side branches. Our results may be relevant to the mechanisms by which ducts proliferate in response to hepatic injury and to the hypercholeresis that occurs after experimentally induced bile duct proliferation.
Figures



References
-
- LaRusso NF: Morphology, physiology and biochemistry of biliary epithelia. Toxicol Pathol 1996, 24:84-89 - PubMed
-
- Roberts SK, Ludwig J, LaRusso NF: The pathobiology of biliary epithelia. Gastroenterology 1997, 112:269-279 - PubMed
-
- Alpini G, Phillips JO, LaRusso NF: The biology of biliary epithelia. Arias IM Boyer JL Fausto N Jakoby WB Schachter DA Shafritz DA eds. The Liver: Biology and Pathobiology. 1994, :pp 623-653 Ltd., New York, Raven Press
-
- Birnbaum A, Suchy FJ: The intrahepatic cholangiopathies. Semin Liver Dis 1998, 18:263-269 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

