Acute effect of the dual angiotensin-converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase 24-11 inhibitor mixanpril on insulin sensitivity in obese Zucker rat
- PMID: 11399666
- PMCID: PMC1572809
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704098
Acute effect of the dual angiotensin-converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase 24-11 inhibitor mixanpril on insulin sensitivity in obese Zucker rat
Abstract
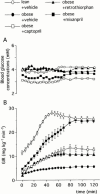
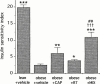
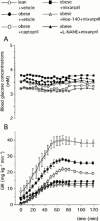
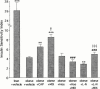
The aim of this study was to determine whether acute dual angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)/neutral endopeptidase 24-11 (NEP) inhibition could improve whole body insulin-mediated glucose disposal (IMGD) more than ACE inhibition alone and whether this effect was mediated by the kinin-nitric oxide (NO) pathway activation. We therefore compared in anaesthetized obese (fa/fa) Zucker rats (ZOs) the effects of captopril (2 mg kg(-1), i.v.+2 mg kg(-1) h(-1)), retrothiorphan (25 mg kg(-1), i.v. +25 mg kg(-1) h(-1)), a selective NEP inhibitor, and mixanpril (25 mg kg(-1), i.v. +25 mg kg(-1) h(-1)), a dual ACE/NEP inhibitor, on IMGD using hyperinsulinaemic euglycaemic clamp technique. The role of the kinin-NO pathway in the effects of mixanpril was tested using a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist (Hoe-140, 300 microg kg(-1)) and a NO-synthase inhibitor (N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester, L-NAME, 10 mg kg(-1) i.v. +10 mg kg(-1) h(-1)) as pretreatments. Insulin sensitivity index (ISI) was lower in ZO controls than in lean littermates. Increases in ISI were observed in captopril- and retrothiorphan-treated ZOs. In mixanpril-treated ZOs, ISI was further increased, compared to captopril- and retrothiorphan-treated ZOs. In ZOs, Hoe-140 and L-NAME alone did not significantly alter and slightly reduced the ISI respectively. Hoe-140 and L-NAME markedly inhibited the ISI improvement induced by mixanpril. These results show that in obese insulin-resistant Zucker rats, under acute conditions, NEP or ACE inhibition can improve IMGD and that dual ACE/NEP inhibition improves IMGD more effectively than does either single inhibition. This effect is linked to an increased activation of the kinin-NO pathway.
Figures
References
-
- ANASTASOPOULOS F., LEUNG R., KLADIS A., JAMES G.M., BRISCOE T.A., GORSKI T.P., CAMBELL D.J. Marked difference between angiotensin-converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase inhibition in vivo by a dual inhibitor of both enzymes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998;284:799–805. - PubMed
-
- BALON T., NADLER J.L. Nitric oxide is present from incubated skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994;77:2519–2521. - PubMed
-
- BARON A.D., BRECHTEL G., WALLACE P., EDELMAN SV. Rate and tissue sites of non insulin and insulin mediated glucose uptake in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1988;255:E769–E774. - PubMed
-
- BARON A.D., ZHU J.S., MARSHALL S., IRSULA O., BRECHTEL G., KEECH C. Insulin resistance after hypertension induced by the nitric oxide synthesis inhibitor L-NMMA in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;269:E709–E715. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

