Ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone from Inula britannica, inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inactivation of NF-kappaB
- PMID: 11399667
- PMCID: PMC1572810
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704099
Ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone from Inula britannica, inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inactivation of NF-kappaB
Abstract
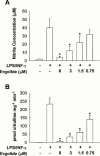
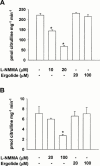
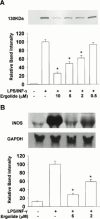
We investigated the mechanism of suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) by ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone from Inula britannica. iNOS activity in cell-free extract of LPS/IFN-gamma-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages was markedly attenuated by the treatment with ergolide. Its inhibitory effect on iNOS was paralleled by decrease in nitrite accumulation in culture medium of LPS/IFN-gamma-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages in a concentration-dependent manner. However, its inhibitory effect does not result from direct inhibition of the catalytic activity of NOS. Ergolide markedly decreased the production of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) in cell-free extract of LPS/IFN-gamma-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages in a concentration-dependent manner, without alteration of the catalytic activity of COX-2 itself. Ergolide decreased the level of iNOS and COX-2 protein, and iNOS mRNA caused by stimulation of LPS/IFN-gamma in a concentration-dependent manner, as measured by Western blot and Northern blot analysis, respectively. Ergolide inhibited nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation, a transcription factor necessary for iNOS and COX-2 expression in response to LPS/IFN-gamma. This effect was accompanied by the parallel reduction of nuclear translocation of subunit p65 of NF-kappaB as well as IkappaB-alpha degradation. In addition, these effects were completely blocked by treatment of cysteine, indicating that this inhibitory effect of ergolide could be mediated by alkylation of NF-kappaB itself or an upstream molecule of NF-kappaB. Ergolide also directly inhibited the DNA-binding activity of active NF-kappaB in LPS/IFN-gamma-pretreated RAW 264.7 macrophages. These results demonstrate that the suppression of NF-kappaB activation by ergolide might be attributed to the inhibition of nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB resulted from blockade of the degradation of IkappaB and the direct modification of active NF-kappaB, leading to the suppression of the expression of iNOS and COX-2, which play important roles in inflammatory signalling pathway.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Acetylbritannilatone suppresses NO and PGE2 synthesis in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 gene expression.Life Sci. 2004 Jun 25;75(6):675-84. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2003.12.022. Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15172177
-
Suppression of the NF-kappaB signalling pathway by ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone, in HeLa cells.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007 Apr;59(4):561-6. doi: 10.1211/jpp.59.4.0011. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17430640
-
1,6-O,O-diacetylbritannilactones inhibits IkappaB kinase beta-dependent NF-kappaB activation.Phytomedicine. 2009 Mar;16(2-3):156-60. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2008.08.003. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Phytomedicine. 2009. PMID: 18926678
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation.Mutat Res. 2001 Sep 1;480-481:243-68. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00183-x. Mutat Res. 2001. PMID: 11506818 Review.
-
Alteration in heme oxygenase-1 and nitric oxide synthase-2 gene expression during endotoxemia in cyclooxygenase-2-deficient mice.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004 Oct;6(5):850-7. doi: 10.1089/ars.2004.6.850. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004. PMID: 15345145 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylbritannilactone Modulates MicroRNA-155-Mediated Inflammatory Response in Ischemic Cerebral Tissues.Mol Med. 2015 Mar 18;21(1):197-209. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00199. Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25811992 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Specificity Phosphatase CDC25B Was Inhibited by Natural Product HB-21 Through Covalently Binding to the Active Site.Front Chem. 2018 Nov 13;6:531. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00531. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2018. PMID: 30555816 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of RACK1-Mediated NLRP3 Oligomerization (Active Conformation) Ameliorates Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jul;12(27):e2411355. doi: 10.1002/advs.202411355. Epub 2025 May 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40349158 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals targeting NF-κB signaling: Potential anti-cancer interventions.J Pharm Anal. 2022 Jun;12(3):394-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2021.07.002. Epub 2021 Jul 6. J Pharm Anal. 2022. PMID: 35811622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential role of sesquiterpene lactones isolated from medicinal plants in the treatment of the metabolic syndrome - A review.S Afr J Bot. 2020 Dec;135:240-251. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2020.08.020. Epub 2020 Sep 16. S Afr J Bot. 2020. PMID: 32963416 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BAEUERLE P.A., BAICHWAL V.R. NF-κB as a frequent target for immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory molecules. Adv Immuno. 1997;65:111–137. - PubMed
-
- BAEUERLE P.A., BALTIMORE D. IκB: a specific inhibitor of the NF-κB transcription factor. Science. 1988;242:540–546. - PubMed
-
- BAEUERLE P.A., BALTIMORE D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- BAEUERLE P.A., HENKEL T. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

