The C6-2B glioma cell P2Y(AC) receptor is pharmacologically and molecularly identical to the platelet P2Y(12) receptor
- PMID: 11399669
- PMCID: PMC1572816
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704114
The C6-2B glioma cell P2Y(AC) receptor is pharmacologically and molecularly identical to the platelet P2Y(12) receptor
Abstract
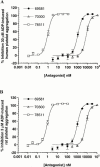
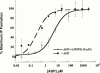
P2Y receptor activation in many cell types leads to phospholipase C activation and accumulation of inositol phosphates, while in blood platelets, C6-2B glioma cells, and in B10 microvascular endothelial cells a P2Y receptor subtype, which couples to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, historically termed P2Y(AC), (P2T(AC) or P(2T) in platelets) has been identified. Recently, this receptor has been cloned and designated P2Y(12) in keeping with current P2 receptor nomenclature. Three selective P(2T) receptor antagonists, with a range of affinities, inhibited ADP-induced aggregation of washed human or rat platelets, in a concentration-dependent manner, with a rank order of antagonist potency (pIC(50), human: rat) of AR-C78511 (8.5 : 9.1)>AR-C69581 (6.2 : 6.0)>AR-C70300 (5.4 : 5.1). However, these compounds had no effect on ADP-induced platelet shape change. All three antagonists had no significant effect on the ADP-induced inositol phosphate formation in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells stably expressing the P2Y(1) receptor, when used at concentrations that inhibit platelet aggregation. These antagonists also blocked ADP-induced inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in rat platelets and C6-2B cells with identical rank orders of potency and overlapping concentration - response curves. RT - PCR and nucleotide sequence analyses revealed that the C6-2B cells express the P2Y(12) mRNA. These data demonstrate that the P2Y(AC) receptor in C6-2B cells is pharmacologically identical to the P2T(AC) receptor in rat platelets.
Figures
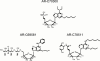


Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning of the platelet P2T(AC) ADP receptor: pharmacological comparison with another ADP receptor, the P2Y(1) receptor.Mol Pharmacol. 2001 Sep;60(3):432-9. Mol Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11502873
-
Activity of adenosine diphosphates and triphosphates on a P2Y(T) -type receptor in brain capillary endothelial cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jan;132(1):173-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703816. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11156575 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and second messenger signalling selectivities of cloned P2Y receptors.J Auton Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;16(6):319-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1996.tb00044.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 9131407
-
The P2 receptors and congenital platelet function defects.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2005 Apr;31(2):168-73. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-869522. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2005. PMID: 15852220 Review.
-
Molecular recognition at adenine nucleotide (P2) receptors in platelets.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2005 Apr;31(2):205-16. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-869526. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2005. PMID: 15852224 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential regulation of ca(2+) signaling and membrane trafficking by multiple p2 receptors in brown adipocytes.J Membr Biol. 2005 Oct;207(3):131-42. doi: 10.1007/s00232-005-0808-x. J Membr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16550484
-
Increased platelet activation and thrombosis in transgenic mice expressing constitutively active P2Y12.J Thromb Haemost. 2012 Oct;10(10):2149-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04894.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22906019 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by neuronal P2Y receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Feb;135(3):673-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704514. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11834615 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of P2Y receptor-activated signal transduction pathways in G protein-dependent signalling networks.Purinergic Signal. 2006 Sep;2(3):451-69. doi: 10.1007/s11302-006-9008-0. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Purinergic Signal. 2006. PMID: 18404483 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Platelets: Harmful or Incidental Bystanders of the Tumor Microenvironment?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;14(9):2192. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092192. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565321 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AKBAR G.K.M., DASARI V.R., WEBB T.E., AYYANATHAN K., PILLARISETTI K., SANDHU A.K., ATHWAL R.S., DANIEL J.L., ASHBY B., BARNARD E.A., KUNAPULI S.P. Molecular cloning of a novel P2 purinoceptor from human erythroleukemia cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:18363–18367. - PubMed
-
- AYYANATHAN K., WEBB T.E., SANDHU A.K., ATHWAL R.S., BARNARD E.A., KUNAPULI S.P. Cloning and chromosomal localization of human P2Y1 purinoceptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996;218:783–788. - PubMed
-
- BJORNSON C.R., RIETZE R.L., REYNOLDS B.A., MAGLI M.C., VESCOVI A.L. Turning brain into blood: a hematopoietic fate adopted by adult neural stem cells in vivo [see comments] Science. 1999;283:534–537. - PubMed
-
- BOYER J.L., LAZAROWSKI E.R., CHEN X.-H., HARDEN T.K. Identification of a P2Y-purinergic receptor that inhibits adenylyl cyclase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993;267:1140–1146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

