Activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase by gram-negative flagellin
- PMID: 11401982
- PMCID: PMC98515
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4424-4429.2001
Activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase by gram-negative flagellin
Abstract
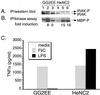
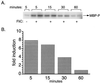
Flagellin from various species of gram-negative bacteria activates monocytes to produce proinflammatory cytokines. We have analyzed the pathway by which Salmonella enteritidis flagellin (FliC) activates murine and human monocyte/macrophage-like cell lines. Since lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the principal immune stimulatory component of gram-negative bacteria, is known to signal through Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), we tested the possibility that FliC also signals via TLR4. When murine HeNC2 cells were stimulated with LPS in the presence of a neutralizing anti-TLR4 monoclonal antibody, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and nitric oxide (NO) production were markedly reduced. In contrast, FliC-mediated TNF-alpha and NO production were minimally affected by the anti-TLR4 antibody. Furthermore, FliC, unlike LPS, stimulated TNF-alpha production in the TLR4 mutant cell line, GG2EE, indicating that TLR4 is not essential for FliC-mediated signaling. To test the possibility that FliC signals via another TLR, we measured FliC-mediated activation of interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase (IRAK), a central component in IL-1R/TLR signaling. FliC induced IRAK activation in HeNC2 and GG2EE cells as well as in the human promonocytic cell line THP-1. IRAK activation was rapid in HeNC2 cells, with maximal activity observed after 5 min of treatment with FliC. In addition, FliC-mediated IRAK activation exhibited the same concentration dependence as was demonstrated for the induction of TNF-alpha. These results represent the first demonstration of IRAK activation by a purified bacterial protein and strongly suggest that a TLR distinct from TLR4 is involved in the macrophage inflammatory response to FliC.
Figures



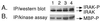
References
-
- Aderem A, Ulevitch R J. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000;406:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Akashi S, Shimazu R, Ogata H, Nagai Y, Takeda K, Kimoto M, Miyake K. Cell surface expression and lipopolysaccharide signaling via the toll-like receptor 4-MD-2 complex on mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 2000;164:3471–3475. - PubMed
-
- Aliprantis A O, Yang R, Mark M, Sugget S, Devaux B, Radolf J D, Klimpel G R, Godowski P, Zychlinsky A. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor 2. Science. 1999;285:736–739. - PubMed
-
- Blasi E, Radzioch D, Durum S K, Varesio L. A murine macrophage cell line, immortalized by v-raf and v-myc oncogenes, exhibits normal macrophage functions. Eur J Immunol. 1987;17:1491–1498. - PubMed
-
- Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel D V. TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature. 1996;383:443–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

