Brucella abortus cyclic beta-1,2-glucan mutants have reduced virulence in mice and are defective in intracellular replication in HeLa cells
- PMID: 11401996
- PMCID: PMC98529
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4528-4535.2001
Brucella abortus cyclic beta-1,2-glucan mutants have reduced virulence in mice and are defective in intracellular replication in HeLa cells
Abstract
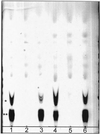
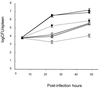
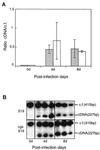
Null cyclic beta-1,2-glucan synthetase mutants (cgs mutants) were obtained from Brucella abortus virulent strain 2308 and from B. abortus attenuated vaccinal strain S19. Both mutants show greater sensitivity to surfactants like deoxycholic acid, sodium dodecyl sulfate, and Zwittergent than the parental strains, suggesting cell surface alterations. Although not to the same extent, both mutants display reduced virulence in mice and defective intracellular multiplication in HeLa cells. The B. abortus S19 cgs mutant was completely cleared from the spleens of mice after 4 weeks, while the 2308 mutant showed a 1.5-log reduction of the number of brucellae isolated from the spleens after 12 weeks. These results suggest that cyclic beta-1,2-glucan plays an important role in the residual virulence of the attenuated B. abortus S19 strain. Although the cgs mutant was cleared from the spleens earlier than the wild-type parental strain (B. abortus S19) and produced less inflammatory response, its ability to confer protection against the virulent strain B. abortus 2308 was fully retained. Equivalent levels of induction of spleen gamma interferon mRNA and anti-lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of immunoglobulin G2a (IgG2a) subtype antibodies were observed in mice injected with B. abortus S19 or the cgs mutant. However, the titer of anti-LPS antibodies of the IgG1 subtype induced by the cgs mutant was lower than that observed with the parental S19 strain, thus suggesting that the cgs mutant induces a relatively exclusive Th1 response.
Figures



References
-
- Alton G G, Jones L M, Angus R D, Verger J M. Techniques for the brucellosis laboratory. Paris, France: INRA; 1988.
-
- Briones G, Iñón de Ianino N, Steinberg M, Ugalde R A. Periplasmic cyclic 1,2-β-glucan in Brucella spp. is not osmoregulated. Microbiology. 1997;143:1115–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

