In vivo visualization of bacterial colonization, antigen expression, and specific T-cell induction following oral administration of live recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 11402006
- PMCID: PMC98539
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4618-4626.2001
In vivo visualization of bacterial colonization, antigen expression, and specific T-cell induction following oral administration of live recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
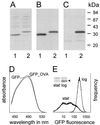
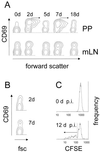
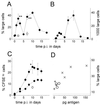
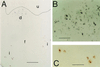
Live attenuated Salmonella strains that express a foreign antigen are promising oral vaccine candidates. Numerous genetic modifications have been empirically tested, but their effects on immunogenicity are difficult to interpret since important in vivo properties of recombinant Salmonella strains such as antigen expression and localization are incompletely characterized and the crucial early inductive events of an immune response to the foreign antigen are not fully understood. Here, methods were developed to directly localize and quantitate the in situ expression of an ovalbumin model antigen in recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium using two-color flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. In parallel, the in vivo activation, blast formation, and division of ovalbumin-specific CD4(+) T cells were followed using a well-characterized transgenic T-cell receptor mouse model. This combined approach revealed a biphasic induction of ovalbumin-specific T cells in the Peyer's patches that followed the local ovalbumin expression of orally administered recombinant Salmonella cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Interestingly, intact Salmonella cells and cognate T cells seemed to remain in separate tissue compartments throughout induction, suggesting a transport of killed Salmonella cells from the colonized subepithelial dome area to the interfollicular inductive sites. The findings of this study will help to rationally optimize recombinant Salmonella strains as efficacious live antigen carriers for oral vaccination.
Figures
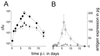
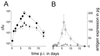

Similar articles
-
Regulated antigen expression in live recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strongly affects colonization capabilities and specific CD4(+)-T-cell responses.Infect Immun. 2001 Dec;69(12):7493-500. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7493-7500.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11705925 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of ovalbumin-specific tolerance by oral administration of Lactococcus lactis secreting ovalbumin.Gastroenterology. 2007 Aug;133(2):517-28. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.04.073. Epub 2007 May 3. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17681173
-
Gamma interferon-independent effects of interleukin-12 on immunity to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2007 Dec;75(12):5753-62. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00971-07. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17875635 Free PMC article.
-
Peyer's patch dendritic cells capturing oral antigen interact with antigen-specific T cells and induce gut-homing CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells in Peyer's patches.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Dec;1029:366-70. doi: 10.1196/annals.1309.020. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15681783
-
T cell receptor-transgenic mouse models for studying cellular immune responses to Salmonella in vivo.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003 Jul 15;37(2-3):105-9. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00064-6. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12832113 Review.
Cited by
-
Stable, site-specific fluorescent tagging constructs optimized for burkholderia species.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Nov;76(22):7635-40. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01188-10. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20851961 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-induced antibody isotypes are skewed by impaired CD4 T cell and invariant NKT cell effector responses in MyD88-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2009 Aug 15;183(4):2252-60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804011. Epub 2009 Jul 20. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19620295 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity to intracellular Salmonella depends on surface-associated antigens.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(10):e1002966. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002966. Epub 2012 Oct 18. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23093937 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neutrophils in murine salmonellosis.Infect Immun. 2004 Jan;72(1):468-77. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.1.468-477.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 14688128 Free PMC article.
-
Development of protective immunity to Salmonella, a mucosal pathogen with a systemic agenda.Mucosal Immunol. 2011 Jul;4(4):371-82. doi: 10.1038/mi.2011.2. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Mucosal Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21307847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjamin W H, Jr, Hall P, Roberts S J, Briles D E. The primary effect of the Ity locus is on the rate of growth of Salmonella typhimurium that are relatively protected from killing. J Immunol. 1990;144:3143–3151. - PubMed
-
- Bumann D, Hueck C, Aebischer T, Meyer T F. Recombinant live Salmonella spp. for human vaccination against heterologous pathogens. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000;27:357–364. - PubMed
-
- Chatfield S N, Charles I G, Makoff A J, Oxer M D, Dougan G, Pickard D, Slater D, Fairweather N F. Use of the nirB promoter to direct the stable expression of heterologous antigens in Salmonella oral vaccine strains: development of a single-dose oral tetanus vaccine. Biotechnology. 1992;10:888–892. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Inobe J, Weiner H L. Inductive events in oral tolerance in the TCR transgenic adoptive transfer model. Cell Immunol. 1997;178:62–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

