In vivo visualization of bacterial colonization, antigen expression, and specific T-cell induction following oral administration of live recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 11402006
- PMCID: PMC98539
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4618-4626.2001
In vivo visualization of bacterial colonization, antigen expression, and specific T-cell induction following oral administration of live recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
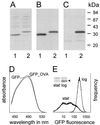
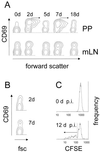
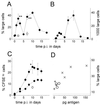
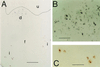
Live attenuated Salmonella strains that express a foreign antigen are promising oral vaccine candidates. Numerous genetic modifications have been empirically tested, but their effects on immunogenicity are difficult to interpret since important in vivo properties of recombinant Salmonella strains such as antigen expression and localization are incompletely characterized and the crucial early inductive events of an immune response to the foreign antigen are not fully understood. Here, methods were developed to directly localize and quantitate the in situ expression of an ovalbumin model antigen in recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium using two-color flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. In parallel, the in vivo activation, blast formation, and division of ovalbumin-specific CD4(+) T cells were followed using a well-characterized transgenic T-cell receptor mouse model. This combined approach revealed a biphasic induction of ovalbumin-specific T cells in the Peyer's patches that followed the local ovalbumin expression of orally administered recombinant Salmonella cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Interestingly, intact Salmonella cells and cognate T cells seemed to remain in separate tissue compartments throughout induction, suggesting a transport of killed Salmonella cells from the colonized subepithelial dome area to the interfollicular inductive sites. The findings of this study will help to rationally optimize recombinant Salmonella strains as efficacious live antigen carriers for oral vaccination.
Figures
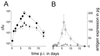
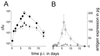

References
-
- Benjamin W H, Jr, Hall P, Roberts S J, Briles D E. The primary effect of the Ity locus is on the rate of growth of Salmonella typhimurium that are relatively protected from killing. J Immunol. 1990;144:3143–3151. - PubMed
-
- Bumann D, Hueck C, Aebischer T, Meyer T F. Recombinant live Salmonella spp. for human vaccination against heterologous pathogens. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000;27:357–364. - PubMed
-
- Chatfield S N, Charles I G, Makoff A J, Oxer M D, Dougan G, Pickard D, Slater D, Fairweather N F. Use of the nirB promoter to direct the stable expression of heterologous antigens in Salmonella oral vaccine strains: development of a single-dose oral tetanus vaccine. Biotechnology. 1992;10:888–892. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Inobe J, Weiner H L. Inductive events in oral tolerance in the TCR transgenic adoptive transfer model. Cell Immunol. 1997;178:62–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

