Complete DNA sequence of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype 0:8 low-calcium-response plasmid reveals a new virulence plasmid-associated replicon
- PMID: 11402007
- PMCID: PMC98540
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4627-4638.2001
Complete DNA sequence of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype 0:8 low-calcium-response plasmid reveals a new virulence plasmid-associated replicon
Abstract
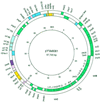
The complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the Yersinia enterocolitica serotype 0:8 low-calcium-response (LCR) plasmid, pYVe8081, were determined. The 67,720-bp plasmid encoded all the genes known to be part of the LCR stimulon except for ylpA. Eight of 13 intact open reading frames of unknown function identified in pYVe8081 had homologues in Yersinia pestis plasmid pCD1 or in Y. enterocolitica serotype 0:9 plasmid pYVe227. A region of approximately 17 kbp showed no DNA identity to pCD1 or pYVe227 and contained six potential new genes, a possible new replicon, and two intact insertion sequence (IS) elements. One intact IS element, ISYen1, was a new IS belonging to the IS256 family. Several vestigial IS elements appeared different from the IS distribution seen in the other LCR plasmids. The RepA proteins encoded by Y. enterocolitica serotype 0:8 pYVeWA and pYVe8081 were identical. The putative pYVe8081 replicon showed significant homology to the IncL/M replicon of pMU407.1 but was only distantly related to the replicons of pCD1 and pYVe227. In contrast, the putative partitioning genes of pYVe8081 showed 97% DNA identity to the spy/sopABC loci of pCD1 and pYVe227. Sequence analysis suggests that Yersinia LCR plasmids are from a common ancestor but that Y. enterocolitica serotype 0:8 plasmid replicons may have evolved independently via cointegrate formation following a transposition event. The change in replicon structure is predicted to change the incompatibility properties of Y. enterocolitica serotype 0:8 plasmids from those of Y. enterocolitica serotype 0:9 and Y. pestis LCR plasmids.
Figures




Similar articles
-
DNA sequencing and analysis of the low-Ca2+-response plasmid pCD1 of Yersinia pestis KIM5.Infect Immun. 1998 Oct;66(10):4611-23. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4611-4623.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9746557 Free PMC article.
-
DNA sequence and analysis of the pYVa127/90 virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica strain A127/90.Res Microbiol. 2003 Oct;154(8):553-7. doi: 10.1016/S0923-2508(03)00147-5. Res Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14527656
-
Structural organization of virulence-associated plasmids of Yersinia pestis.J Bacteriol. 1998 Oct;180(19):5192-202. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.19.5192-5202.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9748454 Free PMC article.
-
Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness.Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64-87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. Rev Infect Dis. 1987. PMID: 3547579 Review.
-
Interactions between Yersinia enterocolitica and the host with special reference to virulence plasmid encoded adhesion and humoral immunity.Dan Med Bull. 1992 Apr;39(2):155-72. Dan Med Bull. 1992. PMID: 1611921 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered Ca(2+) regulation of Yop secretion in Yersinia enterocolitica after DNA adenine methyltransferase overproduction is mediated by Clp-dependent degradation of LcrG.J Bacteriol. 2006 Oct;188(20):7072-81. doi: 10.1128/JB.00583-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 17015646 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and molecular characterization of YsaL (Ye3555): a novel negative regulator of YsaN ATPase in type three secretion system of enteropathogenic bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 4;8(10):e75028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075028. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24124464 Free PMC article.
-
Intraspecific diversity of Yersinia pestis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004 Apr;17(2):434-64. doi: 10.1128/CMR.17.2.434-464.2004. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15084509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Yersinia pestis with macrophages: limitations in YopJ-dependent apoptosis.Infect Immun. 2006 Jun;74(6):3239-50. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00097-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16714551 Free PMC article.
-
Serogroup-related escape of Yersinia enterocolitica YopE from degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.Infect Immun. 2007 Sep;75(9):4423-31. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00528-07. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17606597 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

