Development of a gene inactivation system for Bacteroides forsythus: construction and characterization of a BspA mutant
- PMID: 11402017
- PMCID: PMC98550
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4686-4690.2001
Development of a gene inactivation system for Bacteroides forsythus: construction and characterization of a BspA mutant
Abstract
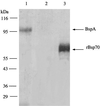
Bacteroides forsythus is a gram-negative anaerobic bacterium associated with periodontitis. The bspA gene encoding a cell surface associated leucine-rich repeat protein (BspA) involved in adhesion to fibronectin and fibrinogen was recently cloned from this bacterium in our laboratory. We now describe the construction of a BspA-defective mutant of B. forsythus. This is the first report describing the generation of a specific gene knockout mutant of B. forsythus, and this procedure should be useful in establishing the identity of virulence-associated factors in these organisms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis vesicles enhance attachment, and the leucine-rich repeat BspA protein is required for invasion of epithelial cells by "Tannerella forsythia".Infect Immun. 2006 Sep;74(9):5023-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00062-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16926393 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, expression, and sequencing of a cell surface antigen containing a leucine-rich repeat motif from Bacteroides forsythus ATCC 43037.Infect Immun. 1998 Dec;66(12):5703-10. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5703-5710.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9826345 Free PMC article.
-
Tannerella forsythia-induced alveolar bone loss in mice involves leucine-rich-repeat BspA protein.J Dent Res. 2005 May;84(5):462-7. doi: 10.1177/154405910508400512. J Dent Res. 2005. PMID: 15840784
-
Contact-dependent regulation of a Tannerella forsythia virulence factor, BspA, in biofilms.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005 Aug 15;249(2):291-6. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.06.032. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005. PMID: 16006067
-
Recent advances in Bacteroides genetics.Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(1):49-71. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104435. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987. PMID: 3030631 Review.
Cited by
-
An Extracytoplasmic Function Sigma/Anti-Sigma Factor System Regulates β-Glucanase Expression in Tannerella forsythia in Response to Fusobacterium nucleatum Sensing.J Bacteriol. 2022 Dec 20;204(12):e0031322. doi: 10.1128/jb.00313-22. Epub 2022 Nov 30. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 36448787 Free PMC article.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis vesicles enhance attachment, and the leucine-rich repeat BspA protein is required for invasion of epithelial cells by "Tannerella forsythia".Infect Immun. 2006 Sep;74(9):5023-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00062-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16926393 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genome analysis and identification of competitive and cooperative interactions in a polymicrobial disease.ISME J. 2015 Mar;9(3):629-42. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.155. Epub 2014 Aug 29. ISME J. 2015. PMID: 25171331 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a gene knockout system for application in Paenibacillus alvei CCM 2051T, exemplified by the S-layer glycan biosynthesis initiation enzyme WsfP.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 May;75(10):3077-85. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00087-09. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19304819 Free PMC article.
-
Host and bacterial factors linking periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 25;13:980805. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.980805. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ausubel F A, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

