Tom40, the pore-forming component of the protein-conducting TOM channel in the outer membrane of mitochondria
- PMID: 11402060
- PMCID: PMC2192023
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.6.1151
Tom40, the pore-forming component of the protein-conducting TOM channel in the outer membrane of mitochondria
Abstract
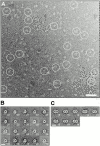
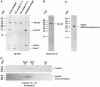
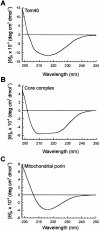
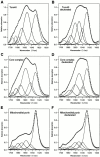
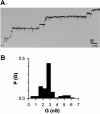
Tom40 is the main component of the preprotein translocase of the outer membrane of mitochondria (TOM complex). We have isolated Tom40 of Neurospora crassa by removing the receptor Tom22 and the small Tom components Tom6 and Tom7 from the purified TOM core complex. Tom40 is organized in a high molecular mass complex of approximately 350 kD. It forms a high conductance channel. Mitochondrial presequence peptides interact specifically with Tom40 reconstituted into planar lipid membranes and decrease the ion flow through the pores in a voltage-dependent manner. The secondary structure of Tom40 comprises approximately 31% beta-sheet, 22% alpha-helix, and 47% remaining structure as determined by circular dichroism measurements and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Electron microscopy of purified Tom40 revealed particles primarily with one center of stain accumulation. They presumably represent an open pore with a diameter of approximately 2.5 nm, similar to the pores found in the TOM complex. Thus, Tom40 is the core element of the TOM translocase; it forms the protein-conducting channel in an oligomeric assembly.
Figures

References
-
- Bathori G., Szabo I., Wolff D., Zoratti M. The high-conductance channels of yeast mitochondrial outer membranesa planar bilayer study. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1996;28:191–198. - PubMed
-
- Benz R., Janko K., Boos W., Läuger P. Formation of large, ion-permeable membrane channels by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli . Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1978;511:305–319. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan S.K. Beta-barrel proteins from bacterial outer membranesstructure, function and refolding. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999;9:455–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

