Focal contacts as mechanosensors: externally applied local mechanical force induces growth of focal contacts by an mDia1-dependent and ROCK-independent mechanism
- PMID: 11402062
- PMCID: PMC2192034
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.6.1175
Focal contacts as mechanosensors: externally applied local mechanical force induces growth of focal contacts by an mDia1-dependent and ROCK-independent mechanism
Abstract
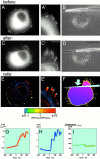
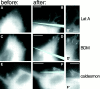
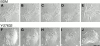
The transition of cell-matrix adhesions from the initial punctate focal complexes into the mature elongated form, known as focal contacts, requires GTPase Rho activity. In particular, activation of myosin II-driven contractility by a Rho target known as Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) was shown to be essential for focal contact formation. To dissect the mechanism of Rho-dependent induction of focal contacts and to elucidate the role of cell contractility, we applied mechanical force to vinculin-containing dot-like adhesions at the cell edge using a micropipette. Local centripetal pulling led to local assembly and elongation of these structures and to their development into streak-like focal contacts, as revealed by the dynamics of green fluorescent protein-tagged vinculin or paxillin and interference reflection microscopy. Inhibition of Rho activity by C3 transferase suppressed this force-induced focal contact formation. However, constitutively active mutants of another Rho target, the formin homology protein mDia1 (Watanabe, N., T. Kato, A. Fujita, T. Ishizaki, and S. Narumiya. 1999. Nat. Cell Biol. 1:136-143), were sufficient to restore force-induced focal contact formation in C3 transferase-treated cells. Force-induced formation of the focal contacts still occurred in cells subjected to myosin II and ROCK inhibition. Thus, as long as mDia1 is active, external tension force bypasses the requirement for ROCK-mediated myosin II contractility in the induction of focal contacts. Our experiments show that integrin-containing focal complexes behave as individual mechanosensors exhibiting directional assembly in response to local force.
Figures






References
-
- Abercrombie M., Dunn G.A. Adhesions of fibroblasts to substratum during contact inhibition observed by interference reflection microscopy. Exp. Cell Res. 1975;92:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Aktories K., Hall A. Botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3a new tool to study low molecular weight GTP-binding proteins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1989;10:415–418. - PubMed
-
- Amano M., Chihara K., Kimura K., Fukata Y., Nakamura N., Matsuura Y., Kaibuchi K. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho- kinase. Science. 1997;275:1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Ayscough K. Use of latrunculin-A, an actin monomer-binding drug. Methods Enzymol. 1998;298:18–25. - PubMed
-
- Balaban N.Q., Schwarz U.S., Riveline D., Goichberg P., Tzur G., Sabanay I., Mahalu D., Safran S., Bershadsky A., Addadi L., Geiger B. Force and focal adhesion assemblya close relationship studied using elastic micro-patterned substrates. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001;3:466–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

