Nodule-specific regulation of phosphatidylinositol transfer protein expression in Lotus japonicus
- PMID: 11402166
- PMCID: PMC135581
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.13.6.1369
Nodule-specific regulation of phosphatidylinositol transfer protein expression in Lotus japonicus
Abstract
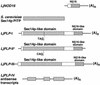
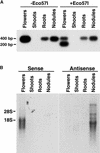
Phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITPs) modulate signal transduction pathways and membrane-trafficking functions in eukaryotes. Here, we describe the characterization of a gene family from Lotus japonicus that encodes a novel class of plant PITP-like proteins (LjPLPs) and that is regulated in an unusual nodule-specific manner. Members of this gene family were identified based on their nucleotide sequence homology with a previously described cDNA, LjNOD16, which encodes the L. japonicus late nodulin Nlj16. Nlj16 or highly related amino acid sequences are shown to constitute C-terminal domains of LjPLPs and are suggested to function as specific plasma membrane targeting modules. The expression patterns of one member of this gene family (LjPLP-IV) revealed that LjNOD16 mRNA synthesis in nodules is the result of the transcriptional activity of a nodule-specific promoter located in an intron of the LjPLP-IV gene. This intron-borne bidirectional promoter also generates nodule-specific antisense transcripts derived from the N-terminal PITP domain coding region of the LjPLP-IV gene. We propose that Nlj16 protein synthesis and LjPLP-IV antisense transcript generation are components of an elaborate mechanism designed to control LjPLP synthesis and/or functioning in nodules.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Lotus japonicus LjNOD70 nodulin gene encodes a protein with similarities to transporters.Plant Mol Biol. 1998 Jul;37(4):651-61. doi: 10.1023/a:1006043428636. Plant Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9687069
-
Novel, highly expressed late nodulin gene (LjNOD16) from Lotus japonicus.Plant Physiol. 1997 Apr;113(4):1081-90. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.4.1081. Plant Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9112769 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the lupin Nodulin-45 promoter: conserved regulatory sequences are important for promoter activity.Plant Mol Biol. 1995 Feb;27(3):457-66. doi: 10.1007/BF00019313. Plant Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7894011
-
Regulators and regulation of legume root nodule development.Plant Physiol. 2000 Oct;124(2):531-40. doi: 10.1104/pp.124.2.531. Plant Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11027704 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Current thoughts on the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein family.FEBS Lett. 2002 Oct 30;531(1):74-80. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03412-9. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12401207 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins and functional specification of lipid signaling pools.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2007;47:27-40. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.12.007. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2007. PMID: 17335879 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sec14-nodulin proteins and the patterning of phosphoinositide landmarks for developmental control of membrane morphogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 May 1;26(9):1764-81. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-10-1475. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25739452 Free PMC article.
-
OsSNDP1, a Sec14-nodulin domain-containing protein, plays a critical role in root hair elongation in rice.Plant Mol Biol. 2013 May;82(1-2):39-50. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0033-4. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Plant Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23456248
-
Novel haplotype description and structural background of the eventual functional significance of the barley beta-amylase gene intron III rearrangements.Theor Appl Genet. 2006 Oct;113(6):1063-79. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0366-3. Epub 2006 Aug 19. Theor Appl Genet. 2006. PMID: 16924478
-
Identification of a novel gene (Hsdr4) involved in water-stress tolerance in wild barley.Plant Mol Biol. 2007 May;64(1-2):17-34. doi: 10.1007/s11103-006-9131-x. Epub 2007 Jan 21. Plant Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17238046
References
-
- Aitken, J.F., van Heusden, G.P.H., Temkin, M., and Dowhan, W. (1990). The gene encoding the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein is essential for cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 4711–4717. - PubMed
-
- Bankaitis, V.A., Aitken, J.F., Cleves, A.E., and Dowhan, W. (1990). An essential role for a phospholipid transfer protein in yeast Golgi function. Nature 347, 561–562. - PubMed
-
- Cleves, A.E., McGee, T.P., and Bankaitis, V.A. (1991). Phospholipid transfer proteins: A biological debut. Trends Cell Biol. 1, 30–34. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham, E., Tan, S.W., Swigart, P., Hsuan, J., Bankaitis, V., and Cockcroft, S. (1996). The yeast and mammalian isoforms of phosphatidylinositol transfer protein can all restore phospholipase C–mediated inositol lipid signaling in cytosol-depleted RBL-2H3 and HL60 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 6589–6593. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

