FPA, a gene involved in floral induction in Arabidopsis, encodes a protein containing RNA-recognition motifs
- PMID: 11402170
- PMCID: PMC135578
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.13.6.1427
FPA, a gene involved in floral induction in Arabidopsis, encodes a protein containing RNA-recognition motifs
Abstract
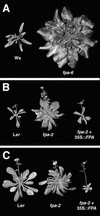
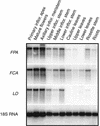
FPA is a gene that regulates flowering time in Arabidopsis via a pathway that is independent of daylength (the autonomous pathway). Mutations in FPA result in extremely delayed flowering. FPA was identified by means of positional cloning. The predicted FPA protein contains three RNA recognition motifs in the N-terminal region. FPA is expressed most strongly in developing tissues, similar to the expression of FCA and LUMINIDEPENDENS, two components of the autonomous pathway previously identified. Overexpression of FPA in Arabidopsis causes early flowering in noninductive short days and creates plants that exhibit a more day-neutral flowering behavior.
Figures


References
-
- Aukerman, M.J., Lee, I., Weigel, D., and Amasino, R.M. (1999). The Arabidopsis flowering-time gene LUMINIDEPENDENS is expressed primarily in regions of cell proliferation and encodes a nuclear protein that regulates LEAFY expression. Plant J. 18, 195–203. - PubMed
-
- Burd, C.G., and Dreyfuss, G. (1994). Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science 265, 615–621. - PubMed
-
- Burn, J.E., Smyth, D.R., Peacock, W.J., and Dennis, E.S. (1993). Genes conferring late flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetica 90, 147–155.
-
- Clarke, J.H., and Dean, C. (1994). Mapping FRI, a locus controlling flowering time and vernalization response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Gen. Genet. 242, 81–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

