Transgenic Arabidopsis plants with decreased activity of fructose-6-phosphate,2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase have altered carbon partitioning
- PMID: 11402203
- PMCID: PMC111165
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.126.2.750
Transgenic Arabidopsis plants with decreased activity of fructose-6-phosphate,2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase have altered carbon partitioning
Abstract
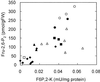
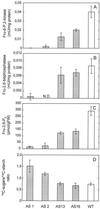
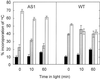
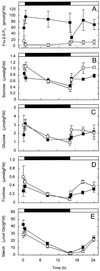
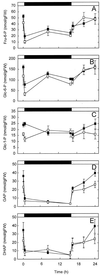
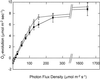
The role of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (Fru-2,6-P(2)) as a regulatory metabolite in photosynthetic carbohydrate metabolism was studied in transgenic Arabidopsis plants with reduced activity of Fru-6-phosphate,2-kinase/Fru-2,6-bisphosphatase. A positive correlation was observed between the Fru-6-phosphate,2-kinase activity and the level of Fru-2,6-P(2) in the leaves. The partitioning of carbon was studied by (14)CO(2) labeling of photosynthetic products. Plant lines with Fru-2,6-P(2) levels down to 5% of the levels observed in wild-type (WT) plants had significantly altered partitioning of carbon between sucrose (Suc) versus starch. The ratio of (14)C incorporated into Suc and starch increased 2- to 3-fold in the plants with low levels of Fru-2,6-P(2) compared with WT. Transgenic plant lines with intermediate levels of Fru-2,6-P(2) compared with WT had a Suc-to-starch labeling ratio similar to the WT. Levels of sugars, starch, and phosphorylated intermediates in leaves were followed during the diurnal cycle. Plants with low levels of Fru-2,6-P(2) in leaves had high levels of Suc, glucose, and Fru and low levels of triose phosphates and glucose-1-P during the light period compared with WT. During the dark period these differences were eliminated. Our data provide direct evidence that Fru-2,6-P(2) affects photosynthetic carbon partitioning in Arabidopsis. Opposed to this, Fru-2,6-P(2) does not contribute significantly to regulation of metabolite levels in darkness.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lack of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate compromises photosynthesis and growth in Arabidopsis in fluctuating environments.Plant J. 2015 Mar;81(5):670-83. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12765. Plant J. 2015. PMID: 25602028
-
Photosynthetic carbon metabolism in leaves of transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) containing decreased amounts of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate.Planta. 2000 Nov;211(6):864-73. doi: 10.1007/s004250000358. Planta. 2000. PMID: 11144272
-
Decreased expression of two key enzymes in the sucrose biosynthesis pathway, cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and sucrose phosphate synthase, has remarkably different consequences for photosynthetic carbon metabolism in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2000 Sep;23(6):759-70. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00847.x. Plant J. 2000. PMID: 10998187
-
Rat liver 6-phosphofructo 2-kinase/fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase: a review of relationships between the two activities of the enzyme.J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(1):1-17. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260102. J Cell Biochem. 1984. PMID: 6096384 Review.
-
Covalent control of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase: insights into autoregulation of a bifunctional enzyme.Protein Sci. 1995 Jun;4(6):1023-37. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040601. Protein Sci. 1995. PMID: 7549867 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate contents were increased in response to salt, water and osmotic stress in leaves of Bruguiera gymnorrhiza by differential changes in the activity of the bifunctional enzyme 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphate 2-phosphatase.Plant Mol Biol. 2003 Sep;53(1-2):51-9. doi: 10.1023/B:PLAN.0000009264.06359.34. Plant Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14756306
-
Changes in Lolium perenne transcriptome during cold acclimation in two genotypes adapted to different climatic conditions.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Oct 17;15:250. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0643-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 26474965 Free PMC article.
-
A device for single leaf labelling with CO2 isotopes to study carbon allocation and partitioning in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Methods. 2013 Nov 19;9(1):45. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-9-45. Plant Methods. 2013. PMID: 24252607 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Studies to Identify Loci and Candidate Genes Controlling Kernel Weight and Length in a Historical United States Wheat Population.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Aug 3;9:1045. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01045. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30123226 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Loci and Candidate Genes Responsible for Fiber Length in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) via Association Mapping and Linkage Analyses.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Feb 5;10:53. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00053. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30804954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G. In planta Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. C R Acad Sci III. 1993;316:1194–1199.
-
- Beutler HO. Monosaccharides and Derivatives. In: Bergmeyer HU, editor. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. Vol. 6. Weinheim, Verlag Chemie; 1984. pp. 321–327.
-
- Cséke C, Buchanan BB. An enzyme synthesizing fructose 2,6-bisphosphate occurs in leaves and is regulated by metabolite effectors. FEBS Lett. 1983;155:139–142.
-
- Cséke C, Stitt M, Balogh A, Buchanan BB. A product-regulated fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase occurs in green leaves. FEBS Lett. 1983;162:103–106.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

