Comprehensive expression profile analysis of the Arabidopsis Hsp70 gene family
- PMID: 11402207
- PMCID: PMC111169
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.126.2.789
Comprehensive expression profile analysis of the Arabidopsis Hsp70 gene family
Abstract
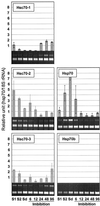
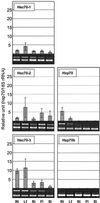
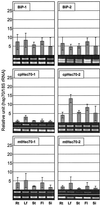
We isolated cDNA clones for two nuclear-encoded, organellar members of the Arabidopsis hsp70 gene family, mtHsc70-2 (AF217458) and cpHsc70-2 (AF217459). Together with the completion of the genome sequence, the hsp70 family in Arabidopsis consists of 14 members unequally distributed among the five chromosomes. To establish detailed expression data of this gene family, a comprehensive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis for 11 hsp70s was conducted including analysis of organ-specific and developmental expression and expression in response to temperature extremes. All hsp70s showed 2- to 20-fold induction by heat shock treatment except cpHsc70-1 and mtHsc70-1, which were unchanged or repressed. The expression profiles in response to low temperature treatment were more diverse than those evoked by heat shock treatment. Both mitochondrial and all cytosolic members of the family except Hsp70b were strongly induced by low temperature, whereas endoplasmic reticulum and chloroplast members were not induced or were slightly repressed. Developmentally regulated expression of the heat-inducible Hsp70 in mature dry seed and roots in the absence of temperature stress suggests prominent roles in seed maturation and root growth for this member of the hsp70 family. This reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis establishes the complex differential expression pattern for the hsp70s in Arabidopsis that portends specialized functions even among members localized to the same subcellular compartment.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Structural organization of the spinach endoplasmic reticulum-luminal 70-kilodalton heat-shock cognate gene and expression of 70-kilodalton heat-shock genes during cold acclimation.Plant Physiol. 1994 Apr;104(4):1359-70. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.4.1359. Plant Physiol. 1994. PMID: 8016266 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and expression of two heat-shock protein genes (HSC70/HSP70) from Prenant's schizothoracin (Schizothorax prenanti).Fish Physiol Biochem. 2015 Apr;41(2):573-85. doi: 10.1007/s10695-015-0030-4. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25690871
-
Arabidopsis stromal 70-kD heat shock proteins are essential for plant development and important for thermotolerance of germinating seeds.Plant Physiol. 2008 Mar;146(3):1231-41. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.114496. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18192441 Free PMC article.
-
A hitchhiker's guide to the human Hsp70 family.Cell Stress Chaperones. 1996 Apr;1(1):23-8. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(1996)001<0023:ahsgtt>2.3.co;2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 1996. PMID: 9222585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic aspects of the hsp70 multigene family in vertebrates.Experientia. 1994 Nov 30;50(11-12):987-1001. doi: 10.1007/BF01923453. Experientia. 1994. PMID: 7988674 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of heat stress responsive gene expression levels for early selection of heat tolerant cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jun 4;14(6):11871-94. doi: 10.3390/ijms140611871. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23736694 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of Hsp70 superfamily proteins of rice (Oryza sativa).Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013 Jul;18(4):427-37. doi: 10.1007/s12192-012-0395-6. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013. PMID: 23264228 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal Growth of Zygophyllum dumosum Boiss.: Summer Dormancy Is Associated with Loss of the Permissive Epigenetic Marker Dimethyl H3K4 and Extensive Reduction in Proteins Involved in Basic Cell Functions.Plants (Basel). 2018 Jul 15;7(3):59. doi: 10.3390/plants7030059. Plants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30011962 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of the Hsp70 gene family in allopolyploid rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) compared with its diploid progenitors.PeerJ. 2019 Aug 20;7:e7511. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7511. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31497395 Free PMC article.
-
Gradual soil water depletion results in reversible changes of gene expression, protein profiles, ecophysiology, and growth performance in Populus euphratica, a poplar growing in arid regions.Plant Physiol. 2007 Feb;143(2):876-92. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.088708. Epub 2006 Dec 8. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17158588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almoguera C, Prieto-Dapena P, Jordano J. Dual regulation of a heat shock promoter during embryogenesis: stage-dependent role of heat shock elements. Plant J. 1998;13:437–446. - PubMed
-
- Boorstein WR, Ziegelhoffer T, Craig EA. Molecular evolution of the hsp70 multigene family. J Mol Evol. 1994;38:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Brodsky JL. Post-translational protein translocation: not all hsc70s are created equal. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:122–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

