Timing of metamorphosis and the onset of the negative feedback loop between the thyroid gland and the pituitary is controlled by type II iodothyronine deiodinase in Xenopus laevis
- PMID: 11404476
- PMCID: PMC34671
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.131198998
Timing of metamorphosis and the onset of the negative feedback loop between the thyroid gland and the pituitary is controlled by type II iodothyronine deiodinase in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
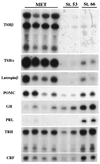
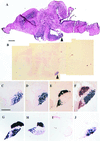
Two important features of amphibian metamorphosis are the sequential response of tissues to different concentrations of thyroid hormone (TH) and the development of the negative feedback loop between the pituitary and the thyroid gland that regulates TH synthesis by the thyroid gland. At the climax of metamorphosis in Xenopus laevis (when the TH level is highest), the ratio of the circulating precursor thyroxine (T4) to the active form 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T3) in the blood is many times higher than it is in tissues. This difference is because of the conversion of T4 to T3 in target cells of the tadpole catalyzed by the enzyme type II iodothyronine deiodinase (D2) and the local effect (cell autonomy) of this activity. Limb buds and tails express D2 early and late in metamorphosis, respectively, correlating with the time that these organs undergo TH-induced change. T(3) is required to complete metamorphosis because the peak concentration of T4 that is reached at metamorphic climax cannot induce the final morphological changes. At the climax of metamorphosis, D2 expression is activated specifically in the anterior pituitary cells that express the genes for thyroid-stimulating hormone but not in the cells that express proopiomelanocortin. Physiological concentrations of T3 but not T4 can suppress thyrotropin subunit beta gene expression. The timing and the remarkable specificity of D2 expression in the thyrotrophs of the anterior pituitary coupled with the requirement for locally synthesized T3 strongly support a role for D2 in the onset of the negative feedback loop at the climax of metamorphosis.
Figures

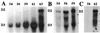
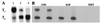
Similar articles
-
Regulation of thyroid hormone sensitivity by differential expression of the thyroid hormone receptor during Xenopus metamorphosis.Genes Cells. 2012 Aug;17(8):645-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2012.01614.x. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Genes Cells. 2012. PMID: 22686326
-
Expression of type II iodothyronine deiodinase marks the time that a tissue responds to thyroid hormone-induced metamorphosis in Xenopus laevis.Dev Biol. 2004 Feb 1;266(1):87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.10.005. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 14729480
-
Regulation of pituitary thyrotropin gene expression during Xenopus metamorphosis: negative feedback is functional throughout metamorphosis.J Endocrinol. 2004 Aug;182(2):273-85. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1820273. J Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15283688
-
The role of deiodinases in amphibian metamorphosis.Thyroid. 2005 Aug;15(8):815-21. doi: 10.1089/thy.2005.15.815. Thyroid. 2005. PMID: 16131324 Review.
-
Functional neuroanatomy of thyroid hormone feedback in the human hypothalamus and pituitary gland.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006 Jun 7;251(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2006.03.042. Epub 2006 May 16. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16707210 Review.
Cited by
-
How thyroid hormones and their inhibitors affect cartilage growth and shape in the frog Xenopus laevis.J Anat. 2019 Jan;234(1):89-105. doi: 10.1111/joa.12897. Epub 2018 Nov 20. J Anat. 2019. PMID: 30456781 Free PMC article.
-
Iodothyronine deiodinase enzyme activities in bone.Bone. 2008 Jul;43(1):126-134. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.03.019. Epub 2008 Apr 4. Bone. 2008. PMID: 18468505 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Hormone-disrupting Effects and the Amphibian Metamorphosis Assay.J Toxicol Pathol. 2012 Mar;25(1):1-9. doi: 10.1293/tox.25.1. J Toxicol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22481853 Free PMC article.
-
Retardation of cochlear maturation and impaired hair cell function caused by deletion of all known thyroid hormone receptors.J Neurosci. 2001 Dec 15;21(24):9792-800. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-24-09792.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11739587 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Role of GATA2 in the Negative Regulation of Type 2 Deiodinase Gene by Liganded Thyroid Hormone Receptor β2 in Thyrotroph.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 16;10(11):e0142400. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142400. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26571013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buscaglia M, Leloup J, deLuze A. In: Metamorphosis. Balls M, Bownes M, editors. New York: Clarendon; 1985. pp. 273–293.
-
- Regard E, Taurog A, Nakashima T. Endocrinology. 1978;102:674–684. - PubMed
-
- Dodd M H I, Dodd J M. In: Physiology of the Amphibia. Lofts B, editor. III. New York: Academic; 1976. pp. 467–599.
-
- Kollros J J. Am Zool. 1961;1:107–114.
-
- Nieuwkoop P D, Faber J. Normal Table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin) Amsterdam: Elsevier Biomedical; 1956.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

