Desbutyl-benflumetol, a novel antimalarial compound: in vitro activity in fresh isolates of Plasmodium falciparum from Thailand
- PMID: 11408230
- PMCID: PMC90607
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.7.2106-2109.2001
Desbutyl-benflumetol, a novel antimalarial compound: in vitro activity in fresh isolates of Plasmodium falciparum from Thailand
Abstract
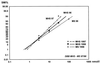
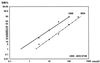
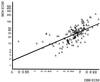
Desbutyl-benflumetol (DBB) is a novel antimalarial compound closely related to benflumetol (lumefantrine), of which it is a putative metabolite. The in vitro response of Plasmodium falciparum to DBB was studied in Mae Hong Son and Mae Sot, in northwest Thailand, in 1997 and 1998. In total, 155 fresh isolates were successfully tested using the World Health Organization standard in vitro microtest system (Mark II). The mean 50% effective concentration (EC(50)) and 90% effective concentration of DBB were 6.36 and 31.09 nmol/liter, respectively. The comparison of the activity of DBB and benflumetol yielded a highly significant potency ratio of 4.52, corresponding to a more than four times higher efficacy of DBB. A considerable potency difference was found between isolates from Mae Hong Son and those from Mae Sot, reflecting lesser sensitivity in the area with marked resistance to mefloquine and quinine. This observation is also supported by a highly significant activity correlation with benflumetol (P < 0.001) and to a similar degree with mefloquine (P < 0.001), reflecting a close relationship of DBB with the class II aryl amino alcohol blood schizontocides. A less distinct association was also found with artemisinin, which was significant only at the EC(50) level, and there was no correlation at all with chloroquine. DBB is a promising antimalarial compound that merits further investigation in order to define its practical therapeutic potential.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergism between monodesbutyl-benflumetol and artemisinin in Plasmodium falciparum in vitro.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008;120(19-20 Suppl 4):80-4. doi: 10.1007/s00508-008-1034-1. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008. PMID: 19066779
-
Interaction between lumefantrine and monodesbutyl-benflumetol in Plasmodium falciparum in vitro.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008;120(19-20 Suppl 4):85-9. doi: 10.1007/s00508-008-1080-8. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008. PMID: 19066780
-
Comparative study on the in vitro activity of lumefantrine and desbutyl-benflumetol in fresh isolates of Plasmodium vivax from Thailand.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2004;116 Suppl 4:47-52. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2004. PMID: 15683043
-
Synergism of desbutyl-benflumetol and retinol against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2005;117 Suppl 4:39-44. doi: 10.1007/s00508-005-0446-4. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2005. PMID: 16416384 Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro activities of benflumetol against 158 Senegalese isolates of Plasmodium falciparum in comparison with those of standard antimalarial drugs.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Feb;43(2):418-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.2.418. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 9925550 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synergism between monodesbutyl-benflumetol and artemisinin in Plasmodium falciparum in vitro.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008;120(19-20 Suppl 4):80-4. doi: 10.1007/s00508-008-1034-1. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008. PMID: 19066779
-
Interaction between lumefantrine and monodesbutyl-benflumetol in Plasmodium falciparum in vitro.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008;120(19-20 Suppl 4):85-9. doi: 10.1007/s00508-008-1080-8. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008. PMID: 19066780
-
Stereoselectivity in the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the chiral antimalarial drugs.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42(15):1359-82. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200342150-00004. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003. PMID: 14674788 Review.
-
Desbutyl-lumefantrine is a metabolite of lumefantrine with potent in vitro antimalarial activity that may influence artemether-lumefantrine treatment outcome.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Mar;55(3):1194-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01312-10. Epub 2011 Jan 3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21199927 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic interaction between monodesbutyl-benflumetol and retinol in Plasmodium falciparum.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2007;119(19-20 Suppl 3):53-9. doi: 10.1007/s00508-007-0870-8. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2007. PMID: 17987359
References
-
- Alin M H, Björkman A, Wernsdorfer W H. Synergism of benflumetol and artemether in Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;61:439–445. - PubMed
-
- Hatz C, Abdulla S, Mull R, Schellenberg D, Gathmann I, Kibatala P, Beck H-P, Tanner M, Royce C. Efficacy and safety of CGP 56697 (artemether and benflumetol) compared with chloroquine to treat acute falciparum malaria in Tanzanian children aged 1–5 years. Trop Med Int Health. 1998;3:498–504. - PubMed
-
- Jiao X, Liu G, Shan C O, Li X W, Gathmann I, Royce C. Phase II trial in China of a new, rapidly-acting and oral antimalarial, CGP 56697, for the treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1997;28:476–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

