Lysosomal hydrolase mannose 6-phosphate uncovering enzyme resides in the trans-Golgi network
- PMID: 11408573
- PMCID: PMC37329
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.6.1623
Lysosomal hydrolase mannose 6-phosphate uncovering enzyme resides in the trans-Golgi network
Abstract
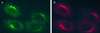
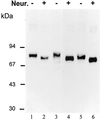
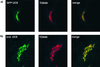
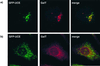
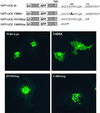
A crucial step in lysosomal biogenesis is catalyzed by "uncovering" enzyme (UCE), which removes a covering N-acetylglucosamine from the mannose 6-phosphate (Man-6-P) recognition marker on lysosomal hydrolases. This study shows that UCE resides in the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and cycles between the TGN and plasma membrane. The cytosolic domain of UCE contains two potential endocytosis motifs: (488)YHPL and C-terminal (511)NPFKD. YHPL is shown to be the more potent of the two in retrieval of UCE from the plasma membrane. A green-fluorescent protein-UCE transmembrane-cytosolic domain fusion protein colocalizes with TGN 46, as does endogenous UCE in HeLa cells, showing that the transmembrane and cytosolic domains determine intracellular location. These data imply that the Man-6-P recognition marker is formed in the TGN, the compartment where Man-6-P receptors bind cargo and are packaged into clathrin-coated vesicles.
Figures


References
-
- Benmerah A, Begue B, Dautry-Varsat A, Cerf-Bensussan N. The ear of α-adaptin interacts with the COOH-terminal domain of the Eps 15 protein. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:12111–12116. - PubMed
-
- Berger EG, Aegerter E, Mandel T, Hauri HP. Monoclonal antibodies to soluble, human milk galactosyltransferase (lactose synthase A protein) Carbohydr Res. 1986;149:23–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

