fMRI investigation of sentence comprehension by eye and by ear: modality fingerprints on cognitive processes
- PMID: 11410952
- PMCID: PMC6872122
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.1036
fMRI investigation of sentence comprehension by eye and by ear: modality fingerprints on cognitive processes
Abstract
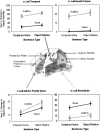
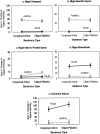
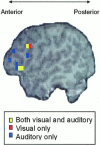
The neural substrate underlying reading vs. listening comprehension of sentences was compared using fMRI. One way in which this issue was addressed was by comparing the patterns of activation particularly in cortical association areas that classically are implicated in language processing. The precise locations of the activation differed between the two modalities. In the left inferior frontal gyrus (Broca's area), the activation associated with listening was more anterior and inferior than the activation associated with reading, suggesting more semantic processing during listening comprehension. In the left posterior superior and middle temporal region (roughly, Wernicke's area), the activation for listening was closer to primary auditory cortex (more anterior and somewhat more lateral) than the activation for reading. In several regions, the activation was much more left lateralized for reading than for listening. In addition to differences in the location of the activation, there were also differences in the total amount of activation in the two modalities in several regions. A second way in which the modality comparison was addressed was by examining how the neural systems responded to comprehension workload in the two modalities by systematically varying the structural complexity of the sentences to be processed. Here, the distribution of the workload increase associated with the processing of additional structural complexity was very similar across the two input modalities. The results suggest a number of subtle differences in the cognitive processing underlying listening vs. reading comprehension.
Copyright 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Awh E, Jonides J, Smith EE, Schumacher EH, Koeppe RA, Katz S (1996): Dissociation of storage and rehearsal in verbal working memory: evidence from positron emission tomography. Psychol Sci 7: 25–31.
-
- Bavelier D, Corina D, Jezzard P, Padmanabhan S, Clark VP, Karni A, Prinster A, Braun A, Lalwani A, Rauschecker JP, Turner R, Neville H (1997): Sentence reading: a functional MRI study at 4 Tesla. J Cogn Neurosci 9: 664–686. - PubMed
-
- Caplan D, Alpert N, Waters G (1998): Effects of syntactic structure and propositional number on patterns of regional cerebral blood flow. J Cogn Neurosci 10: 541–552. - PubMed
-
- Caplan D, Alpert N, Waters G (1999): PET studies of syntactic processing with auditory sentence presentation. Neuroimage 9: 343–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

