Quantitative proton MR spectroscopic imaging in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 11415908
- PMCID: PMC7974787
Quantitative proton MR spectroscopic imaging in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Abstract
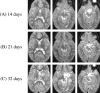
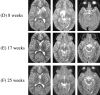
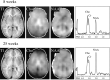
Serial MR imaging and quantitative proton MR spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) findings of a 4-year-old boy with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) are reported. Over a 2-month period characterized by an initial illness and two relapses, each with full recovery, MR imaging exhibited the appearance and disappearance of multifocal lesions throughout the CNS that correlated only partly with the neurologic impairment. During one relapse, MRSI revealed low levels of N-acetylaspartate (NAA) within the regions of prolonged T2 signal intensity. All other metabolites were normal. At follow-up, the MR imaging and MRSI abnormalities had fully resolved. MRSI might play an important role in the diagnosis of ADEM, as well as in the elucidation of underlying pathophysiologic processes in this poorly defined disorder of children. This case demonstrates that reduced levels of NAA are not always associated with neuronal loss, irreversible tissue damage, or poor neurologic outcome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging and proton MR spectroscopy in the characterization of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis.Neuroradiology. 2007 Feb;49(2):177-83. doi: 10.1007/s00234-006-0164-2. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Neuroradiology. 2007. PMID: 17131116
-
Delayed MR imaging changes in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001 Jun-Jul;22(6):1117-24. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. PMID: 11415907 Free PMC article.
-
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, multiphasic disseminated encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis in children.Brain. 2000 Dec;123 Pt 12:2407-22. doi: 10.1093/brain/123.12.2407. Brain. 2000. PMID: 11099444 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis.J Child Neurol. 2012 Nov;27(11):1408-25. doi: 10.1177/0883073812455104. Epub 2012 Aug 21. J Child Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22914374 Review.
-
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis.Semin Pediatr Infect Dis. 2003 Apr;14(2):90-5. doi: 10.1053/spid.2003.127225. Semin Pediatr Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12881796 Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging neuroinflammation? A perspective from MR spectroscopy.Brain Pathol. 2014 Nov;24(6):654-64. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12197. Brain Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25345895 Free PMC article.
-
Childhood obstructive sleep apnea associates with neuropsychological deficits and neuronal brain injury.PLoS Med. 2006 Aug;3(8):e301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030301. PLoS Med. 2006. PMID: 16933960 Free PMC article.
-
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in childhood brainstem lesions.Childs Nerv Syst. 2007 Mar;23(3):305-14. doi: 10.1007/s00381-006-0221-5. Epub 2006 Sep 16. Childs Nerv Syst. 2007. PMID: 16983570
-
[Value of MR spectroscopy in infectious and inflammatory brain diseases].Radiologe. 2010 Sep;50(9):784-90. doi: 10.1007/s00117-009-1949-1. Radiologe. 2010. PMID: 20924742 German.
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in pediatric neuroradiology: clinical and research applications.Pediatr Radiol. 2010 Jan;40(1):3-30. doi: 10.1007/s00247-009-1450-z. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Pediatr Radiol. 2010. PMID: 19937238
References
-
- Nasr JT, Andriola MR, Coyle PK. ADEM: literature review and case report of acute psychosis presentation. Pediatr Neurol 2000;22:8-18 - PubMed
-
- Kesselring J, Miller DH, Robb SA. et al. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: MRI findings and the distinction from multiple sclerosis. Brain 1990;113:291-302 - PubMed
-
- Duyn J, Gillen J, Sobering G, van Zijl P, Moonen C. Multislic proton MR spectroscopic imaging of the brain. Radiology 1993;188:277-282 - PubMed
-
- Soher BJ, van Zijl PCM, Duyn JH, Barker PB. Quantitative proton spectroscopic imaging of the human brain. Magn. Reson. Med 1996;35:356-363 - PubMed
-
- Davie CA, Hawkins CP, Barker GJ. et al. Serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in acute multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 1994;117:49-58 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
