Concentration-effect relationships of two infusion rates of the imidazoline antihypertensive agent rilmenidine for blood pressure and development of side-effects in healthy subjects
- PMID: 11421999
- PMCID: PMC2014466
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2001.01387.x
Concentration-effect relationships of two infusion rates of the imidazoline antihypertensive agent rilmenidine for blood pressure and development of side-effects in healthy subjects
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to compare the effect profiles of i.v. administered rilmenidine aimed at the same target plasma concentration, but attained with different rates.
Methods: The study was placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, three-way, cross-over in nine healthy volunteers. All subjects randomly received either a fast infusion, a slow infusion or a placebo infusion. The target concentration was set at 8 ng ml-1 with a fivefold difference in the time to reach the maximum concentration. Saccadic eye movements, electroencephalography (EEG), blood pressure and heart rate were measured every half hour. Drug plasma concentrations, adverse events, salivary flow and visual analogue scales were obtained every hour.
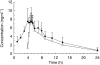
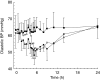
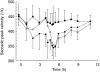
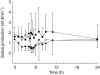
Results: Changes in systolic/diastolic blood pressure at the end of the infusion were (mean +/- s.d.) 13.3 +/- 16.4/7.9 +/- 7.5 mmHg with the fast infusion and 16.3 +/- 12.7/10.2 +/- 7.9 mmHg during the slow infusion, compared with 0.0 +/- 13.2/1.3 +/- 8.3 mmHg for the placebo occasion. Decrease of saccadic peak velocity (SPV) at the end of the infusion was 18.0 +/- 5.2% during the fast infusion, 23.0 +/- 7.0% with the slow infusion, and 6.1 +/- 5.2% with placebo. PK/PD analysis showed similar concentration-dependent linear reduction in SPV and blood pressure up to the maximum observed rilmenidine plasma level for both the fast and the slow infusion.
Conclusions: The rate of infusion of rilmenidine in healthy volunteers does not influence the PK/PD relationship of saccadic eye movements and blood pressure up to the maximum observed rilmenidine plasma concentrations. Rilmenidine causes clear concentration-dependent blood pressure reductions in healthy volunteers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of rilmenidine and clonidine on the electroencephalogram, saccadic eye movements, and psychomotor function.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995;26 Suppl 2:S48-54. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8642806 Clinical Trial.
-
Concentration-effect relationships of two rilmenidine single-dose infusion rates in hypertensive patients.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002 Oct;72(4):419-28. doi: 10.1067/mcp.2002.127638. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12386644 Clinical Trial.
-
[Rilmenidine sympatholytic activity preserves mental and orthostatic sympathetic response and epinephrine secretion].Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2004 Jul-Aug;97(7-8):786-92. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2004. PMID: 15506067 Clinical Trial. French.
-
I1 imidazoline agonists. General clinical pharmacology of imidazoline receptors: implications for the treatment of the elderly.Drugs Aging. 2000 Aug;17(2):133-59. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200017020-00005. Drugs Aging. 2000. PMID: 10984201 Review.
-
Rilmenidine and vigilance. Review of clinical studies.Am J Med. 1989 Sep 18;87(3C):67S-72S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90509-3. Am J Med. 1989. PMID: 2571296 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers for the effects of benzodiazepines in healthy volunteers.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003 Jan;55(1):39-50. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.t01-10-01714.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12534639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central nervous system effects of the interaction between risperidone (single dose) and the 5-HT6 antagonist SB742457 (repeated doses) in healthy men.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Jun;71(6):907-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.03902.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21223356 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ostermann G, Brisgand B, Schmitt J, Fillastre J-P. Efficacy and acceptability of ril menidine for mild to moderate systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1988;61:76D–80D. - PubMed
-
- Fillastre J-P, Letac B, Galinier F, Le Bihan G, Schwartz J. A multicenter double-blind comparative study of rilmenidine and clonidine in 333 hypertensive patients. Am J Cardiol. 1988;61:81D–85D. - PubMed
-
- Galley P, Manciet G, Hessel J-L, Michel JP. Antihypertensive efficacy and acceptability of rilmenidine in elderly hypertensive patients. Am J Cardiol. 1988;61:86D–90D. - PubMed
-
- Mpoy M, Vandeleene B, Ketelslegers J-M, Lambert AE. Treatment of systemic hypertension in insulin-treated diabetes mellitus with rilmenidine. Am J Cardiol. 1988;61:91D–94D. - PubMed
-
- Beau B, Mahieux F, Paraire M, Laurin S, Brisgand B, Vitou P. Efficacy and safety of rilmenidine for arterial hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1988;61:95D–101D. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

