Pharmacokinetic interaction between mefloquine and ritonavir in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 11422019
- PMCID: PMC2014486
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2001.01393.x
Pharmacokinetic interaction between mefloquine and ritonavir in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the pharmacokinetic interaction between ritonavir and mefloquine.
Methods: Healthy volunteers participated in two separate, nonfasted, three-treatment, three-period, longitudinal pharmacokinetic studies. Study 1 (12 completed): ritonavir 200 mg twice daily for 7 days, 7 day washout, mefloquine 250 mg once daily for 3 days then once weekly for 4 weeks, ritonavir restarted for 7 days simultaneously with the last mefloquine dose. Study 2 (11 completed): ritonavir 200 mg single dose, mefloquine 250 mg once daily for 3 days then once weekly for 2 weeks, ritonavir single dose repeated 2 days after the last mefloquine dose. Erythromycin breath test (ERMBT) was administered with and without drug treatments in study 2.
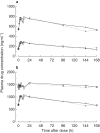
Results: Study 1: Ritonavir caused less than 7% changes with high precision (90% CIs: -12% to 11%) in overall plasma exposure (AUC(0,168 h)) and peak concentration (Cmax) of mefloquine, its two enantiomers, and carboxylic acid metabolite, and in the metabolite/mefloquine and enantiomeric AUC ratios. Mefloquine significantly decreased steady-state ritonavir plasma AUC(0,12 h) by 31%, Cmax by 36%, and predose levels by 43%, and did not affect ritonavir binding to plasma proteins. Study 2: Mefloquine did not alter single-dose ritonavir pharmacokinetics. Less than 8% changes in AUC and Cmax were observed with high variability (90%CIs: -26% to 45%). Mefloquine had no effect on the ERMBT whereas ritonavir decreased activity by 98%.
Conclusions: Ritonavir minimally affected mefloquine pharmacokinetics despite strong inhibition of CYP3A4 activity from a single 200 mg dose. Mefloquine had variable effects on ritonavir pharmacokinetics that were not explained by hepatic CYP3A4 activity or ritonavir protein binding.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Atlanta, GA: 1999. Health Information for International Travel.−2000, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
-
- Hsu A, Granneman GR, Bertz RJ. Ritonavir: clinical pharmacokinetics and interactions with other anti-HIV agents. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1998;35:275–291. - PubMed
-
- Profit L, Eagling VA, Back DJ. Modulation of P-glycoprotein function in human lymphocytes and Caco-2 cell monolayers by HIV-1 protease inhibitors. AIDS. 1999;13:1623–1627. - PubMed
-
- Landmann R, Peytavin G, Leibowitch J, et al. Conference Record of the 12th World AIDS Conference. Geneva, Switzerland: 1998. Ritonavir (RTV) low dosages increases dramatically the saquinavir (SQV-HGC) bioavailability: A PK study in healthy volunteers (HV) p. 824. abstract no. 42257.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

