Flow cytometric microsphere-based immunoassay: analysis of secreted cytokines in whole-blood samples from asthmatics
- PMID: 11427426
- PMCID: PMC96142
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.4.776-784.2001
Flow cytometric microsphere-based immunoassay: analysis of secreted cytokines in whole-blood samples from asthmatics
Abstract
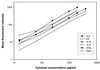
The ability of flow cytometry to resolve multiple parameters was used in a microsphere-based flow cytometric assay for the simultaneous determination of several cytokines in a sample. The flow cytometer microsphere-based assay (FMBA) for cytokines consists of reagents and dedicated software, specifically designed for the quantitative determination of cytokines. We have made several improvements in the multiplex assay: (i) dedicated software specific for the quantitative multiplex assay that processes data automatically, (ii) a stored master calibration curve with a two-point recalibration to adjust the stored curve periodically, and (iii) an internal standard to normalize the detection step in each sample. Overall analytical performance, including sensitivity, reproducibility, and dynamic range, was investigated for interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), and tumor necrosis factor alpha. These assays were found to be reproducible and accurate, with a sensitivity in the picograms-per-milliliter range. Results obtained with FMBA correlate well with commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay data (r > 0.98) for all cytokines assayed. This multiplex assay was applied to the determination of cytokine profiles in whole blood from atopic and nonatopic patients. Our results show that atopic subjects' blood produces more IL-4 (P = 0.003) and less IFN-gamma (P = 0.04) than the blood of nonatopic subjects. However, atopic asthmatic subjects' blood produces significantly more IFN-gamma than that of atopic nonasthmatic subjects (P = 0.03). The results obtained indicate that the FMBA technology constitutes a powerful system for the quantitative, simultaneous determination of secreted cytokines in immune diseases.
Figures






References
-
- Bishop J E, Davis K A. A flow cytometric immunoassay for β2-microglobulin in whole blood. J Immunol Methods. 1997;210:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Broide D H, Lotz M, Cuomo A J, Coburn D A, Federman E C, Wasserman S I. Cytokines in sympomatic asthma airways. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992;5:958–967. - PubMed
-
- Carson R T, Vignali D A A. Simultaneous quantitation of 15 cytokines using multiplexed flow cytometric assay. J Immunol Methods. 1999;227:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Collins D P, Luebering B J, Shaut D M. T-lymphocyte functionality assessed by analysis of cytokine receptor expression, intracellular cytokine expression, and femtomolar detection of cytokine secretion by quantitative flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1998;33:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Defoort J P, Martin M, Casano B, Prato S, Camilla C, Fert V. Simultaneous detection of multiplex-amplified human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA, hepatitis C virus RNA, and hepatitis B virus DNA using a flow cytometer microsphere-based hybridization assay. J Clin Microbiobiol. 2000;38:1066–1077. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

