Detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputa by nested PCR-linked single-strand conformation polymorphism and DNA sequencing
- PMID: 11427578
- PMCID: PMC88194
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.7.2610-2617.2001
Detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputa by nested PCR-linked single-strand conformation polymorphism and DNA sequencing
Abstract
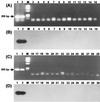
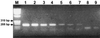
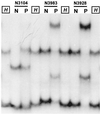
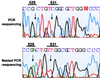
Either PCR-mediated single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis or DNA sequencing of rpoB DNA (157 bp) can be used as a rapid screening method for the detection of mutations related to the rifampin resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. However, due to the nonspecific amplification of rpoB DNA from nontuberculous mycobacteria these methods cannot be directly applied to clinical specimens such as sputa. We developed a nested PCR method that can specifically amplify the rpoB DNA of M. tuberculosis on the basis of rpoB DNA sequences of 44 mycobacteria. Nested PCR-linked SSCP analysis and the DNA sequencing method were applied directly in order to detect M. tuberculosis and determine its rifampin susceptibility in 56 sputa. The results obtained by nested PCR-SSCP and DNA sequencing were concordant with those of conventional drug susceptibility testing and DNA sequencing performed with culture isolates.
Figures

References
-
- Barnes P, Bloch A B, Davidson P T, Snider D E., Jr Tuberculosis in patients with immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1644–1650. - PubMed
-
- British Thoracic Association. A controlled trial of six months chemotherapy in pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982;126:460–462. - PubMed
-
- De Beenhouwer H, Lhiang Z, Jannes G, Mijs W, Machtelinckx L, Rossau R, Traore H, Portalels F. Rapid detection of rifampin resistance in sputum and biopsy specimens from tuberculosis patients by PCR and line probe assay. Tuber Lung Dis. 1995;76:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Des Prez R M, Heim C R. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In: Mandell G L, Douglas R G, Bennett J E, editors. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 2nd ed. New York, N.Y: Churchill Livingstone; 1990. pp. 1877–1906.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

