Mechanics of the mammalian cochlea
- PMID: 11427697
- PMCID: PMC3590856
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1305
Mechanics of the mammalian cochlea
Abstract
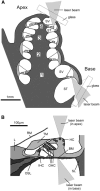
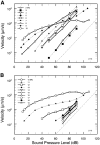
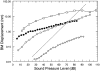
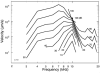
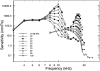
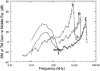
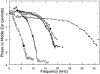
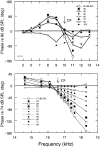
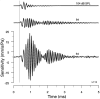
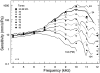
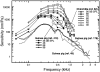
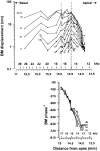
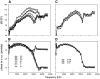
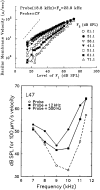
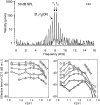
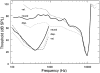
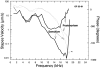
In mammals, environmental sounds stimulate the auditory receptor, the cochlea, via vibrations of the stapes, the innermost of the middle ear ossicles. These vibrations produce displacement waves that travel on the elongated and spirally wound basilar membrane (BM). As they travel, waves grow in amplitude, reaching a maximum and then dying out. The location of maximum BM motion is a function of stimulus frequency, with high-frequency waves being localized to the "base" of the cochlea (near the stapes) and low-frequency waves approaching the "apex" of the cochlea. Thus each cochlear site has a characteristic frequency (CF), to which it responds maximally. BM vibrations produce motion of hair cell stereocilia, which gates stereociliar transduction channels leading to the generation of hair cell receptor potentials and the excitation of afferent auditory nerve fibers. At the base of the cochlea, BM motion exhibits a CF-specific and level-dependent compressive nonlinearity such that responses to low-level, near-CF stimuli are sensitive and sharply frequency-tuned and responses to intense stimuli are insensitive and poorly tuned. The high sensitivity and sharp-frequency tuning, as well as compression and other nonlinearities (two-tone suppression and intermodulation distortion), are highly labile, indicating the presence in normal cochleae of a positive feedback from the organ of Corti, the "cochlear amplifier." This mechanism involves forces generated by the outer hair cells and controlled, directly or indirectly, by their transduction currents. At the apex of the cochlea, nonlinearities appear to be less prominent than at the base, perhaps implying that the cochlear amplifier plays a lesser role in determining apical mechanical responses to sound. Whether at the base or the apex, the properties of BM vibration adequately account for most frequency-specific properties of the responses to sound of auditory nerve fibers.
Figures


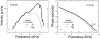
References
-
- Abbas PJ. Effects of stimulus frequency on two-tone suppression: a comparison of physiological and psychophysical results. J Acoust Soc Am. 1978;63:1878–1886. - PubMed
-
- Abbas PJ, Sachs MB. Two-tone suppression in auditory-nerve fibers: extension of a stimulus-response relationship. J Acoust Soc Am. 1976;59:112–122. - PubMed
-
- Allen JB. Two-dimensional cochlear fluid model: new results. J Acoust Soc Am. 1977;61:110–119. - PubMed
-
- Allen JB. Cochlear micromechanics—a physical model of transduction. J Acoust Soc Am. 1980;68:1660–1670. - PubMed
-
- Allen JB, Fahey PF. A second cochlear-frequency map that correlates distortion product and neural tuning measurements. J Acoust Soc Am. 1993;94:809–816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

