N-arginine dibasic convertase is a specific receptor for heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor that mediates cell migration
- PMID: 11432822
- PMCID: PMC125525
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.13.3342
N-arginine dibasic convertase is a specific receptor for heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor that mediates cell migration
Abstract
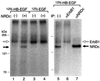
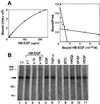
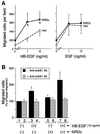
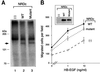
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF), a mitogen and chemotactic factor, binds to two receptor tyrosine kinases, erbB1 and erbB4. Now we demonstrate that HB-EGF also binds to a novel 140 kDa receptor on MDA-MB 453 cells. Purification of this receptor showed it to be identical to N-arginine dibasic convertase (NRDc), a metalloendopeptidase of the M16 family. Binding to cell surface NRDc and NRDc in solution was highly specific for HB-EGF among EGF family members. When overexpressed in cells, NRDc enhanced their migration in response to HB-EGF but not to EGF. Conversely, inhibition of endogenous NRDc expression in cells by antisense morpholino oligonucleotides inhibited HB-EGF-induced cell migration. Anti-erbB1 neutralizing antibodies completely abrogated the ability of NRDc to enhance HB-EGF-dependent migration, demonstrating that this NRDc activity was dependent on erbB1 signaling. Although NRDc is a metalloproteinase, enzymatic activity was not required for HB-EGF binding or enhancement of cell migration; neither did NRDc cleave HB-EGF. Together, these results suggest that NRDc is a novel specific receptor for HB-EGF that modulates HB-EGF-induced cell migration via erbB1.
Figures


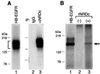
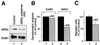
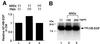
Similar articles
-
The metalloendopeptidase nardilysin (NRDc) is potently inhibited by heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF).Biochem J. 2002 Oct 1;367(Pt 1):229-38. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020822. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12095415 Free PMC article.
-
Nardilysin enhances ectodomain shedding of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor through activation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 13;281(41):31164-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601316200. Epub 2006 Aug 21. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16923819
-
Activation of HER4 by heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor stimulates chemotaxis but not proliferation.EMBO J. 1997 Mar 17;16(6):1268-78. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.6.1268. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9135143 Free PMC article.
-
Nardilysin, a basic residues specific metallopeptidase that mediates cell migration and proliferation.Protein Pept Lett. 2004 Oct;11(5):501-8. doi: 10.2174/0929866043406508. Protein Pept Lett. 2004. PMID: 15544571 Review.
-
TACE/ADAM17 processing of EGFR ligands indicates a role as a physiological convertase.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 May;995:22-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb03207.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12814936 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation and characterization of conditional heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor knockout mice.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 14;4(10):e7461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007461. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19829704 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) therapy for intestinal injury: Application and future prospects.Pathophysiology. 2014 Feb;21(1):95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Dec 15. Pathophysiology. 2014. PMID: 24345808 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor protects mesenchymal stem cells.J Surg Res. 2012 Oct;177(2):359-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.05.016. Epub 2012 May 23. J Surg Res. 2012. PMID: 22658491 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal administration of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in an experimental model of necrotizing enterocolitis decreased both incidence and severity of the disease.World J Pediatr Surg. 2022 Jan 5;5(1):e000345. doi: 10.1136/wjps-2021-000345. eCollection 2022. World J Pediatr Surg. 2022. PMID: 36474622 Free PMC article.
-
NRD1, which encodes nardilysin protein, promotes esophageal cancer cell invasion through induction of MMP2 and MMP3 expression.Cancer Sci. 2014 Jan;105(1):134-40. doi: 10.1111/cas.12316. Epub 2013 Nov 29. Cancer Sci. 2014. PMID: 24168165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham J.A., Damm,D., Bajardi,A., Miller,J., Klagsbrun,M. and Ezekowitz,R.A. (1993) Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor: characterization of rat and mouse cDNA clones, protein domain conservation across species and transcript expression in tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 190, 125–133. - PubMed
-
- Chesneau V., Pierotti,A.R., Barre,N., Creminon,C., Tougard,C. and Cohen,P. (1994a) Isolation and characterization of a dibasic selective metalloendopeptidase from rat testes that cleaves at the amino terminus of arginine residues. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 2056–2061. - PubMed
-
- Chesneau V., Pierotti,A.R., Prat,A., Gaudoux,F., Foulon,T. and Cohen,P. (1994b) N-arginine dibasic convertase (NRD convertase): a newcomer to the family of processing endopeptidases. Biochimie, 76, 234–240. - PubMed
-
- Chesneau V., Prat,A., Segretain,D., Hospital,V., Dupaix,A., Foulon,T., Jegou,B. and Cohen,P. (1996) NRD convertase: a putative processing endoprotease associated with the axoneme and the manchette in late spermatids. J. Cell Sci., 109, 2737–2745. - PubMed
-
- Das S.K., Wang,X.N., Paria,B.C., Damm,D., Abraham,J.A., Klagsbrun, M., Andrews,G.K. and Dey,S.K. (1994) Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor gene is induced in the mouse uterus temporally by the blastocyst solely at the site of its apposition: a possible ligand for interaction with blastocyst EGF-receptor in implantation. Development, 120, 1071–1083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

