In vivo co-localisation of MBNL protein with DMPK expanded-repeat transcripts
- PMID: 11433021
- PMCID: PMC55763
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2766
In vivo co-localisation of MBNL protein with DMPK expanded-repeat transcripts
Abstract
Myotonic dystrophy (DM1) is the most common form of adult muscular dystrophy and is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. The genetic basis of DM1 is the expansion of a CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of a protein kinase gene (DMPK). The molecular mechanism by which this expanded repeat produces the pathophysiology of DM1 remains unknown. Transcripts from the expanded allele accumulate as foci in the nucleus of DM1 cells and it has been suggested that these transcript foci sequester cellular proteins that are required for normal nuclear function. We have investigated the role of three RNA-binding proteins, CUG-BP, hnRNP C and MBNL, as possible sequestered factors. Using a combination of indirect immunofluorescence to detect endogenous proteins and overexpression of proteins with green fluorescent protein (GFP) tags we have shown that CUG-BP and hnRNP C do not co-localise with expanded repeat foci in DM1 cell lines. However, GFP-tagged MBNL does itself form foci in DM1 cell lines and co-localises with the foci of expanded repeat transcripts. GFP-tagged MBNL does not appear as foci in non-DM1 cell lines. This work provides further support for the involvement of MBNL in DM1.
Figures
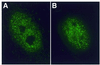

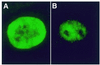
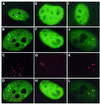
References
-
- Harper P.S. (1989) Myotonic dystrophy, 2nd edn. Saunders, London; Philadelphia.
-
- Brook J.D., McCurrach,M.E., Harley,H.G., Buckler,A.J., Church,D., Aburatani,H., Hunter,K., Stanton,V.P., Thirion,J.P., Hudson,T. et al. (1992) Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell, 68, 799–808. - PubMed
-
- Krahe R., Ashizawa,T., Abbruzzese,C., Roeder,E., Carango,P., Giacanelli,M., Funanage,V.L. and Siciliano,M.J. (1995) Effect of myotonic dystrophy trinucleotide repeat expansion on DMPK transcription and processing. Genomics, 28, 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Fu Y.H., Friedman,D.L., Richards,S., Pearlman,J.A., Gibbs,R.A., Pizzuti,A., Ashizawa,T., Perryman,M.B., Scarlato,G., Fenwick,R.G. et al. (1993) Decreased expression of myotonin-protein kinase messenger RNA and protein in adult form of myotonic dystrophy. Science, 260, 235–238. - PubMed
-
- Jansen G., Groenen,P.J., Bachner,D., Jap,P.H., Coerwinkel,M., Oerlemans,F., van den Broek,W., Gohlsch,B., Pette,D., Plomp,J.J. et al. (1996) Abnormal myotonic dystrophy protein kinase levels produce only mild myopathy in mice. Nat. Genet., 13, 316–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

