Significantly higher activity of a cytoplasmic hammerhead ribozyme than a corresponding nuclear counterpart: engineered tRNAs with an extended 3' end can be exported efficiently and specifically to the cytoplasm in mammalian cells
- PMID: 11433023
- PMCID: PMC55762
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2780
Significantly higher activity of a cytoplasmic hammerhead ribozyme than a corresponding nuclear counterpart: engineered tRNAs with an extended 3' end can be exported efficiently and specifically to the cytoplasm in mammalian cells
Abstract
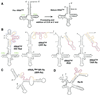
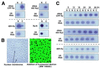
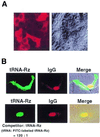
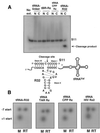
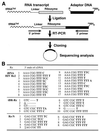
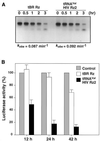
Hammerhead ribozymes were expressed under the control of similar tRNA promoters, localizing transcripts either in the cytoplasm or the nucleus. The tRNA(Val)-driven ribozyme (tRNA-Rz; tRNA with extra sequences at the 3' end) that has been used in our ribozyme studies was exported efficiently into the cytoplasm and ribozyme activity was detected only in the cytoplasmic fraction. Both ends of the transported tRNA-Rz were characterized comprehensively and the results confirmed that tRNA-Rz had unprocessed 5' and 3' ends. Furthermore, it was also demonstrated that the activity of the exported ribozyme was significantly higher than that of the ribozyme which remained in the nucleus. We suggest that it is possible to engineer tRNA-Rz, which can be exported to the cytoplasm based on an understanding of secondary structures, and then tRNA-driven ribozymes may be co-localized with their target mRNAs in the cytoplasm of mammalian cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction of a ribozyme-expression system that effectively transports ribozymes to the cytoplasm.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 2000;(44):203-4. doi: 10.1093/nass/44.1.203. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 2000. PMID: 12903339
-
Transport of intracellularly active ribozymes to the cytoplasm.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001 Aug;48 Suppl 1:S96-101. doi: 10.1007/s002800100314. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11587376
-
Ribozyme expression systems.Methods Mol Biol. 2004;252:195-207. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-746-7:195. Methods Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15017050
-
Use of ribozymes in cellular aging research.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;371:209-26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-361-5_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17634584 Review.
-
The many faces of the hairpin ribozyme: structural and functional variants of a small catalytic RNA.IUBMB Life. 2012 Jan;64(1):36-47. doi: 10.1002/iub.575. Epub 2011 Nov 30. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22131309 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant 7SL RNA and tRNA(Tyr) genes with inserted antisense sequences are efficiently expressed in an in vitro transcription system from Nicotiana tabacum cells.Plant Mol Biol. 2002 Nov;50(4-5):713-23. doi: 10.1023/a:1019905730397. Plant Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12374302
-
Endogenous expression of a high-affinity pseudoknot RNA aptamer suppresses replication of HIV-1.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Sep 15;30(18):4001-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf522. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12235384 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-specific RNAi mitigates phenotypic progression in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Ther. 2009 Sep;17(9):1563-73. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.123. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19532137 Free PMC article.
-
Functional repair of a mutant chloride channel using a trans-splicing ribozyme.J Clin Invest. 2002 Dec;110(12):1783-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI16481. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12488428 Free PMC article.
-
A functional gene discovery in the Fas-mediated pathway to apoptosis by analysis of transiently expressed randomized hybrid-ribozyme libraries.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Aug 15;30(16):3609-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf476. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12177303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uhlenbeck O.C. (1987) A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature, 328, 596–600. - PubMed
-
- Haseloff J. and Gerlach,W.L. (1988) Simple RNA enzymes with new and highly specific endoribonuclease activities. Nature, 334, 585–591. - PubMed
-
- Symons R.H. (1989) Self-cleavage of RNA in the replication of small pathogens of plants and animals. Trends Biochem. Sci., 14, 445–450. - PubMed
-
- Pyle A.M. (1993) Ribozymes: a distinct class of metalloenzymes. Science, 261, 709–714. - PubMed
-
- Sawata S., Komiyama,M. and Taira,K. (1995) Kinetic evidence based on solvent isotope effects for the nonexistence of a proton-transfer process in reactions catalyzed by a hammerhead ribozyme: implications to the double-metal-ion mechanism of catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 117, 2357–2358.

