Amino acid-base interactions: a three-dimensional analysis of protein-DNA interactions at an atomic level
- PMID: 11433033
- PMCID: PMC55782
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2860
Amino acid-base interactions: a three-dimensional analysis of protein-DNA interactions at an atomic level
Abstract
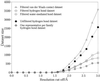
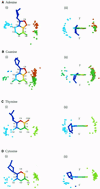
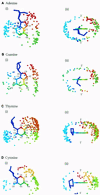
To assess whether there are universal rules that govern amino acid-base recognition, we investigate hydrogen bonds, van der Waals contacts and water-mediated bonds in 129 protein-DNA complex structures. DNA-backbone interactions are the most numerous, providing stability rather than specificity. For base interactions, there are significant base-amino acid type correlations, which can be rationalised by considering the stereochemistry of protein side chains and the base edges exposed in the DNA structure. Nearly two-thirds of the direct read-out of DNA sequences involves complex networks of hydrogen bonds, which enhance specificity. Two-thirds of all protein-DNA interactions comprise van der Waals contacts, compared to about one-sixth each of hydrogen and water-mediated bonds. This highlights the central importance of these contacts for complex formation, which have previously been relegated to a secondary role. Although common, water-mediated bonds are usually non-specific, acting as space-fillers at the protein-DNA interface. In conclusion, the majority of amino acid-base interactions observed follow general principles that apply across all protein-DNA complexes, although there are individual exceptions. Therefore, we distinguish between interactions whose specificities are 'universal' and 'context-dependent'. An interactive Web-based atlas of side chain-base contacts provides access to the collected data, including analyses and visualisation of the three-dimensional geometry of the interactions.
Figures
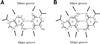



References
-
- Pabo C.O. and Sauer,R.T. (1982) Protein–DNA recognition. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 53, 293–321. - PubMed
-
- Matthews B.W. (1988) No code for recognition. Nature, 335, 294–295. - PubMed
-
- Pabo C.O. and Sauer,R.T. (1992) Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 61, 1053–1095. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki M. (1994) A framework for the DNA–protein recognition code of the probe helix in transcription factors: the chemical and stereochemical rules. Structure, 2, 317–326. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

