c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis
- PMID: 11435459
- PMCID: PMC209341
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12466
c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest 2001 Dec;108(12):1883
Abstract
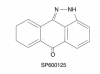
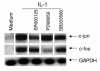
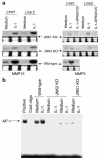
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades are involved in inflammation and tissue destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In particular, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is highly activated in RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes and synovium. However, defining the precise function of this kinase has been difficult because a selective JNK inhibitor has not been available. We now report the use of a novel selective JNK inhibitor and JNK knockout mice to determine the function of JNK in synoviocyte biology and inflammatory arthritis. The novel JNK inhibitor SP600125 (anthra[1,9-cd]pyrazol-6(2H)-one) completely blocked IL-1--induced accumulation of phospho-Jun and induction of c-Jun transcription in synoviocytes. Furthermore, AP-1 binding and collagenase mRNA accumulation were completely suppressed by SP600125. In contrast, complete inhibition of p38 had no effect, and ERK inhibition had only a modest effect. The essential role of JNK was confirmed in cultured synoviocytes from JNK1 knockout mice and JNK2 knockout mice, each of which had a partial defect in IL-1--induced AP-1 activation and collagenase-3 expression. Administration of SP600125 modestly decreased the rat paw swelling in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. More striking was the near-complete inhibition of radiographic damage that was associated with decreased AP-1 activity and collagenase-3 gene expression. Therefore, JNK is a critical MAPK pathway for IL-1--induced collagenase gene expression in synoviocytes and in joint arthritis, indicating that JNK is an important therapeutic target for RA.
Figures


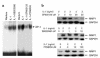
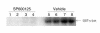

Comment in
-
The potential of signal transduction inhibitors for the treatment of arthritis: Is it all just JNK?J Clin Invest. 2001 Jul;108(2):181-3. doi: 10.1172/JCI13508. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11457869 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Robinson MJ, Cobb MH. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:180–185. - PubMed
-
- Seger R, Krebs EG. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995;9:726–735. - PubMed
-
- Fanger GR, Gerwins P, Widmann C, Jarpe MB, Johnson GL. MEKKs, GCKs, MLKs, PAKs, TAKs, and tpls: upstream regulators of the c-Jun amino-terminal kinases? Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997;7:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Hibi M, Lin A, Smeal T, Minden A, Karin M. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 1993;7:2149–2160. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS. Rheumatoid arthritis. Shaun Ruddy, editor. Scientific American Inc. New York, New York, USA. Scientific American Medicine. 1998;15:2.1–2.14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

