Adenosine deaminase deficiency increases thymic apoptosis and causes defective T cell receptor signaling
- PMID: 11435465
- PMCID: PMC209335
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI10360
Adenosine deaminase deficiency increases thymic apoptosis and causes defective T cell receptor signaling
Abstract
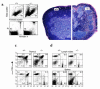
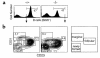
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency in humans results in a severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). This immunodeficiency is associated with severe disturbances in purine metabolism that are thought to mediate lymphotoxicity. The recent generation of ADA-deficient (ADA(-/-)) mice has enabled the in vivo examination of mechanisms that may underlie the SCID resulting from ADA deficiency. We demonstrate severe depletion of T and B lymphocytes and defects in T and B cell development in ADA(-/-) mice. T cell apoptosis was abundant in thymi of ADA(-/-) mice, but no increase in apoptosis was detected in the spleen and lymph nodes of these animals, suggesting that the defect is specific to developing thymocytes. Studies of mature T cells recovered from spleens of ADA(-/-) mice revealed that ADA deficiency is accompanied by TCR activation defects of T cells in vivo. Furthermore, ex vivo experiments on ADA(-/-) T cells demonstrated that elevated adenosine is responsible for this abnormal TCR signaling. These findings suggest that the metabolic disturbances seen in ADA(-/-) mice affect various signaling pathways that regulate thymocyte survival and function. Experiments with thymocytes ex vivo confirmed that ADA deficiency reduces tyrosine phosphorylation of TCR-associated signaling molecules and blocks TCR-triggered calcium increases.
Figures






References
-
- Giblett ER, Anderson JE, Cohen F, Pollara B, Meuwissen HJ. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972;2:1067–1069. - PubMed
-
- Giblett ER, Ammann AJ, Wara DW, Sandman R, Diamond LK. Nucleoside-phosphorylase deficiency in a child with severely defective T-cell immunity and normal B-cell immunity. Lancet. 1975;1:1010–1013. - PubMed
-
- Buckley RH, et al. Human severe combined immunodeficiency: genetic, phenotypic, and functional diversity in one hundred eight infants. J Pediatr. 1997;130:378–387. - PubMed
-
- Hershfield, M.S., and Mitchell, B.S. 1995. Immunodeficiency diseases caused by adenosine deaminase deficiency and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. In The molecular and metabolic bases of inherited disease. C.R. Scriver, A.L. Beaudet, W.S. Sly, and D. Valle, editors. McGraw-Hill. New York, New York, USA. 1725–1768.
-
- Olah ME, Stiles GL. Adenosine receptor subtypes: characterization and therapeutic regulation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1995;35:581–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

