Virulence plasmid-borne spvB and spvC genes can replace the 90-kilobase plasmid in conferring virulence to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in subcutaneously inoculated mice
- PMID: 11443102
- PMCID: PMC95362
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.15.4652-4658.2001
Virulence plasmid-borne spvB and spvC genes can replace the 90-kilobase plasmid in conferring virulence to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in subcutaneously inoculated mice
Abstract
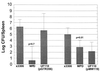
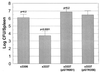
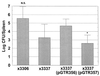
In a mouse model of systemic infection, the spv genes carried on the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium virulence plasmid increase the replication rate of salmonellae in host cells of the reticuloendothelial system, most likely within macrophages. A nonpolar deletion in the spvB gene greatly decreased virulence but could not be complemented by spvB alone. However, a low-copy-number plasmid expressing spvBC from a constitutive lacUV5 promoter did complement the spvB deletion. By examining a series of spv mutations and cloned spv sequences, we deduced that spvB and spvC could be sufficient to confer plasmid-mediated virulence to S. enterica serovar Typhimurium. The spvBC-bearing plasmid was capable of replacing all of the spv genes, as well as the entire virulence plasmid, of serovar Typhimurium for causing systemic infection in BALB/c mice after subcutaneous, but not oral, inoculation. A point mutation in the spvBC plasmid preventing translation but not transcription of spvC eliminated the ability of the plasmid to confer virulence. Therefore, it appears that both spvB and spvC encode the principal effector factors for Spv- and plasmid-mediated virulence of serovar Typhimurium.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Constitutively expressed phoP inhibits mouse-virulence of Salmonella typhimurium in an Spv-dependent manner.Microbiol Immunol. 2000;44(6):447-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2000.tb02519.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10941927
-
The Salmonella typhimurium virulence plasmid encodes a positive regulator of a plasmid-encoded virulence gene.J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7176-85. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7176-7185.1991. J Bacteriol. 1991. PMID: 1657882 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella plasmid virulence gene spvB enhances bacterial virulence by inhibiting autophagy in a zebrafish infection model.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Feb;49:252-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.12.033. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26723267
-
Molecular analysis of spv virulence genes of the Salmonella virulence plasmids.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):825-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01172.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 8483415 Review.
-
Evolution of the virulence plasmids of non-typhoid Salmonella and its association with antimicrobial resistance.Microbes Infect. 2006 Jun;8(7):1931-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2005.12.026. Epub 2006 Mar 27. Microbes Infect. 2006. PMID: 16713725 Review.
Cited by
-
Virulence genes and sanitizers resistance in Salmonella isolates from eggs in southern Brazil.J Food Sci Technol. 2022 Mar;59(3):1097-1103. doi: 10.1007/s13197-021-05113-5. Epub 2021 May 4. J Food Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35153327 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence Gene Profile, Antimicrobial Resistance and Multilocus Sequence Typing of Salmonella enterica Subsp. enterica Serovar Enteritidis from Chickens and Chicken Products.Animals (Basel). 2022 Jan 1;12(1):97. doi: 10.3390/ani12010097. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35011203 Free PMC article.
-
OspF and OspC1 are Shigella flexneri type III secretion system effectors that are required for postinvasion aspects of virulence.Infect Immun. 2006 Oct;74(10):5964-76. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00594-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16988276 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the live vaccine efficacy of virulence plasmid-cured, and phoP- or aroA-deficient Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in mice.J Vet Med Sci. 2015 Feb;77(2):181-6. doi: 10.1292/jvms.14-0013. Epub 2014 Oct 24. J Vet Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25341392 Free PMC article.
-
Next generation genome sequencing reveals phylogenetic clades with different level of virulence among Salmonella Typhimurium clinical human isolates in Hong Kong.BMC Genomics. 2015 Sep 14;16(1):688. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1900-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26370680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coynault C, Robbe-Saule V, Popoff M Y, Norel F. Growth phase and SpvR regulation of transcription of Salmonella typhimurium spvABC virulence genes. Microb Pathog. 1992;13:133–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

