Hsp27 inhibits cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation by sequestering both pro-caspase-3 and cytochrome c
- PMID: 11444529
- PMCID: PMC5964942
- DOI: 10.3727/000000001783992605
Hsp27 inhibits cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation by sequestering both pro-caspase-3 and cytochrome c
Abstract
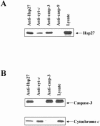
Mitochondrial cytochrome c release in response to pro-apoptotic signals leads to the formation of a cytochrome c/Apaf-1/procaspase-9 complex (the apoptosome) and resultant activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3. Here we demonstrate that the molecular chaperone, Hsp27, inhibits this cytochrome c-mediated activation of caspase-3. Immunodepeletion of Hsp27 from cytochrome c-activated cytosols resulted in decreased caspase activity. Furthermore, immunoprecipitation of Hsp27 resulted in the coprecipitation of both cytochrome c and procaspase-3. In reciprocal experiments, immunoprecipitation of both procaspase-3 and cytochrome c resulted in coprecipitation of Hsp27, indicating two independent interactions. These results point to Hsp27 mediating its inhibition of procaspase-3 activation through its ability to sequester both cytochrome c and procaspase-3, and thus prevent the correct formation/function of the apoptosome complex.
Figures


References
-
- Arrigo A. P.; Landry J. Expression and function of the low molecular weight heat shock proteins. In: The biology of heat shock proteins and molecular chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1994:335–373.
-
- Downs C. A.; Jones L. R.; Heckathorn S. A. Evidence for a novel set of small heat-shock proteins that associates with the mitochondria of murine PC 12 cells and protects NADH:Ubiquinone oxidoreductase from heat and oxidative stress. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 365:344–350; 1999. - PubMed
-
- Garrido C.; Bruey J. M.; Fromentin A.; Hammann A.; Arrigo A. P.; Solary E. Hsp27 inhibits cytochrome c dependent activation of procaspase-9. FASEB J. 13:2061–2070; 1999. - PubMed
-
- Guénal I.; Sidoti-de Fraisse C; Gaumer S.; Mignotte B. Bcl-2 and Hsp27 act at different levels to suppress programmed cell death. Oncogene 15:347–360; 1997. - PubMed
-
- Jäättelä M. Heat shock proteins as cellular lifeguards. Ann. Med. 31:261–271; 1999. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
