Downregulation of constitutive and heavy metal-induced metallothionein-I expression by nuclear factor I
- PMID: 11444530
- PMCID: PMC5964943
- DOI: 10.3727/000000001783992588
Downregulation of constitutive and heavy metal-induced metallothionein-I expression by nuclear factor I
Abstract
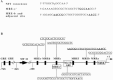
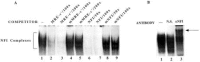
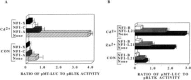
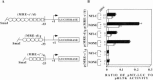
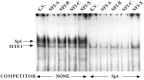
Although the existence of repressor protein(s) involved in the regulation of highly inducible metallothionein-I (MT-I) gene expression has been postulated, none has been identified to date. We considered nuclear factor I (NFL) protein as a potential repressor, as three half-sites for NFI binding are present on MT-I promoter and NFI is known to downregulate several cellular gene promoters. Overexpression of all four isoforms of mouse NFI protein (NFI-A, -B, -C, and -X) suppressed both constitutive and heavy metal-induced activation of the MT-I promoter in HepG2 cells. However, unlike other target genes of NFI, direct interaction of NFI with MT-I promoter is not necessary to mediate its repression. Point mutation of the NFI binding sites within the MT-I promoter that abrogates NFI binding in vitro could not alleviate the repression. Similarly, NFI proteins also repress activity of minimal MT-I promoter deficient in the NFI binding sites. Further, an NFI-C deletion mutant lacking the DNA binding domain continued to repress MT-I promoter. Overexpression of MTF-1, the key trails-acting factor involved in MT-I gene transcription, surmounted NFI-mediated repression of the basal and zinc-induced MT-I promoter activity. These data demonstrate that NFI is a repressor of MT-I expression, where its DNA binding activity is not essential to downregulate the MT-I promoter. Interaction of NFI with another protein(s), probably MTF-I, may be involved in this repression.
Figures



References
-
- Adams A. D.; Choate D. M.; Thompson M. A. NF1-L is the DNA-binding component of the protein complex at the peripherin negative regulatory element. J. Biol. Chem. 270:6975–6983; 1995. [Erratum appears in J. Biol. Chem. 270:19668; 1995] - PubMed
-
- Aiyar A.; Leis J. Modification of the megaprimer method of PCR metagenesis: Improved amplification of the final product. Biotechniques 14:366–369; 1993. - PubMed
-
- Alam J.; Smith A. Heme-hemopexin-mediated induction of metallothionein gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 267:16379–16384; 1992. - PubMed
-
- Andrews G. K. Regulation of metallothionein gene expression by oxidative stress and metal ions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 59:95–104; 2000. - PubMed
-
- Aniskovitch L.; Jacob S. T. Purification and characterization of a rat liver protein that recognizes CCAAT-homologous sequences of the metallothionein promoter and trans-activates this promoter. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 341:337–346; 1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
