Alteration in expression of the rat mitochondrial ATPase 6 gene during Pneumocystis carinii infection
- PMID: 11446902
- PMCID: PMC34520
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-1-8
Alteration in expression of the rat mitochondrial ATPase 6 gene during Pneumocystis carinii infection
Abstract
Background: Pneumocystis carinii causes pneumonia in immunocompromised patients with a high morbidity and mortality rate, but the interaction between this organism and the host cell is not well understood. The purpose of this research was to study the response of host cells to P. carinii infection on a molecular level.
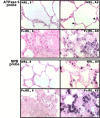
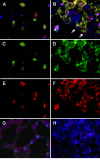
Results: The technique of mRNA differential display was used to detect genes whose expression may be affected by P. carinii infection. The nucleotide sequence of one differentially displayed DNA fragment was found to be identical to that of the rat mitochondrial ATPase 6 gene, which is a subunit of the F0F1-ATP synthase complex. A four-fold increase in expression of this gene was verified by Northern blot analysis of total RNA extracted from P. carinii-infected rat lung versus that from mock-infected rat lung. Localization of the cells containing ATPase 6 mRNA was accomplished by in situ hybridization. In sections of non-infected rat lung, these cells were found lining the distal parts of the respiratory tree and in apical areas of the alveoli. Histological location of these cells suggested that they were Clara cells and type II pneumocytes. This hypothesis was confirmed by co-localizing the mRNAs for ATPase 6 and surfactant protein B (SP-B) to the same cells by two-color fluorescent in situ hybridization.
Conclusions: The ATPase 6 gene is over expressed during P. carinii infection, and type II pneumocytes and Clara cells are the cell types responsible for this over-expression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Upregulation of host mitochondrial ATPase 6 gene in Pneumocystis carinii-infected rat lungs.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1996 Sep-Oct;43(5):38S. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1996.tb04974.x. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8822841 No abstract available.
-
Enhanced lung injury and delayed clearance of Pneumocystis carinii in surfactant protein A-deficient mice: attenuation of cytokine responses and reactive oxygen-nitrogen species.Infect Immun. 2004 Oct;72(10):6002-11. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.6002-6011.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15385504 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of ATP synthase subunit-6, cytochrome c oxidase-III, and NADH dehydrogenase-3 by bright cyclic light in the rat retina.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004 Aug;45(8):2489-96. doi: 10.1167/iovs.03-1081. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. PMID: 15277468
-
Diversity of host species and strains of Pneumocystis carinii is based on rRNA sequences.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1996 Jan;3(1):119-27. doi: 10.1128/cdli.3.1.119-127.1996. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8770515 Free PMC article.
-
[Pneumocystis carinii--diagnosis based on DNA amplification technique].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2004 Nov;17(101):530-3. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2004. PMID: 15754651 Review. Polish.
References
-
- Fishman JA, Samia JA, Fuglestad J, Rose RM. The effects of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins on the attachment of Pneumocystis carinii to lung cell lines. J Protozool. 1991;Suppl 38:34–37. - PubMed
-
- Wisniowski P, Martin WJ., II Interaction of vitronectin with Pneumocystis carinii: evidence for binding via the heparin binding domain. Clin Res. 1992;40:A697. - PubMed
-
- Limper AH, Pottratz ST, Martin WJ., II Modulation of Pneumocystis carinii adherence to cultured lung cells by a mannose-dependent mechanism. J Lab Clin Med. 1991;118:492–499. - PubMed
-
- Koziel H, Baik J, Armstrong MYK, Richards FF, Rose RM. Pneumocystis carinii surface glycoprotein-A is a chemotactic factor for normal human blood monocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;147:A33.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

