Myosin VI isoform localized to clathrin-coated vesicles with a role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis
- PMID: 11447109
- PMCID: PMC125554
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.14.3676
Myosin VI isoform localized to clathrin-coated vesicles with a role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis
Abstract
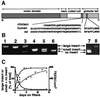
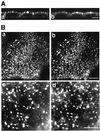
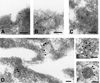
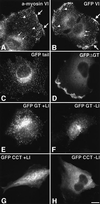
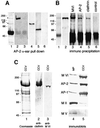
Myosin VI is involved in membrane traffic and dynamics and is the only myosin known to move towards the minus end of actin filaments. Splice variants of myosin VI with a large insert in the tail domain were specifically expressed in polarized cells containing microvilli. In these polarized cells, endogenous myosin VI containing the large insert was concentrated at the apical domain co-localizing with clathrin- coated pits/vesicles. Using full-length myosin VI and deletion mutants tagged with green fluorescent protein (GFP) we have shown that myosin VI associates and co-localizes with clathrin-coated pits/vesicles by its C-terminal tail. Myosin VI, precipitated from whole cytosol, was present in a protein complex containing adaptor protein (AP)-2 and clathrin, and enriched in purified clathrin-coated vesicles. Over-expression of the tail domain of myosin VI containing the large insert in fibroblasts reduced transferrin uptake in transiently and stably transfected cells by >50%. Myosin VI is the first motor protein to be identified associated with clathrin-coated pits/vesicles and shown to modulate clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
Figures



References
-
- Avraham K.B., Hasson,T., Steel,K.P., Kingsley,D.M., Russell,L.B., Mooseker,M.S., Copeland,N.G. and Jenkins,N.A. (1995) The mouse Snell’s waltzer deafness gene encodes an unconventional myosin required for structural integrity of inner ear hair cells. Nature Genet., 11, 369–375. - PubMed
-
- Breckler J., Au,K., Cheng,J., Hasson,T. and Burnside,B. (2000) Novel myosin VI isoform is abundantly expressed in retina. Exp. Eye Res., 70, 121–134. - PubMed
-
- Buss F., Kendrick-Jones,J., Lionne,C., Knight,A.E., Cote,G.P. and Luzio,J.P. (1998) The localization of myosin VI at the Golgi complex and leading edge of fibroblasts and its phosphorylation and recruitment into membrane ruffles of A431 cells after growth factor stimulation. J. Cell Biol., 143, 1535–1545. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

