Heterologous dimerization domains functionally substitute for the double-stranded RNA binding domains of the kinase PKR
- PMID: 11447114
- PMCID: PMC125533
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.14.3728
Heterologous dimerization domains functionally substitute for the double-stranded RNA binding domains of the kinase PKR
Abstract
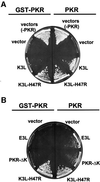
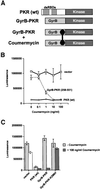
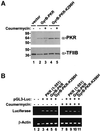
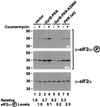
The protein kinase PKR (dsRNA-dependent protein kinase) phosphorylates the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF2alpha to downregulate protein synthesis in virus-infected cells. Two double-stranded RNA binding domains (dsRBDs) in the N-terminal half of PKR are thought to bind the activator double-stranded RNA, mediate dimerization of the protein and target PKR to the ribosome. To investigate further the importance of dimerization for PKR activity, fusion proteins were generated linking the PKR kinase domain to heterologous dimerization domains. Whereas the isolated PKR kinase domain (KD) was non-functional in vivo, expression of a glutathione S-transferase-KD fusion, or co-expression of KD fusions containing the heterodimerization domains of the Xlim-1 and Ldb1 proteins, restored PKR activity in yeast cells. Finally, coumermycin-mediated dimerization of a GyrB-KD fusion protein increased eIF2alpha phosphorylation and inhibited reporter gene translation in mammalian cells. These results demonstrate the critical importance of dimerization for PKR activity in vivo, and suggest that a primary function of double-stranded RNA binding to the dsRBDs of native PKR is to promote dimerization and activation of the kinase domain.
Figures


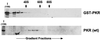

Similar articles
-
trans-Autophosphorylation by the isolated kinase domain is not sufficient for dimerization or activation of the dsRNA-activated protein kinase PKR.Biochemistry. 2004 Aug 31;43(34):11027-34. doi: 10.1021/bi0360105. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15323561
-
Identification and requirement of three ribosome binding domains in dsRNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR).Biochemistry. 1998 Sep 29;37(39):13816-26. doi: 10.1021/bi981472h. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9753471
-
Uncoupling of RNA binding and PKR kinase activation by viral inhibitor RNAs.J Mol Biol. 2006 May 19;358(5):1270-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.03.003. Epub 2006 Mar 20. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16580685
-
PKR and eIF2alpha: integration of kinase dimerization, activation, and substrate docking.Cell. 2005 Sep 23;122(6):823-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.007. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16179248 Review.
-
PKR; a sentinel kinase for cellular stress.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 1;18(45):6112-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203127. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10557102 Review.
Cited by
-
Baculovirus protein PK2 subverts eIF2α kinase function by mimicry of its kinase domain C-lobe.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 11;112(32):E4364-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1505481112. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26216977 Free PMC article.
-
The eIF2α kinases: their structures and functions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Oct;70(19):3493-511. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1252-6. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23354059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PKR and TLR3 trigger distinct signals that coordinate the induction of antiviral apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Aug 15;13(8):707. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05101-3. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35970851 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of protein kinase PKR requires dimerization-induced cis-phosphorylation within the activation loop.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 28;289(9):5747-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.527796. Epub 2013 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24338483 Free PMC article.
-
RNA binding by a novel helical fold of b2 protein from wuhan nodavirus mediates the suppression of RNA interference and promotes b2 dimerization.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(18):9543-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00785-11. Epub 2011 Jul 6. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21734038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertolotti A., Zhang,Y., Hendershot,L., Harding,H. and Ron,D. (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nature Cell Biol., 2, 326–332. - PubMed
-
- Breen J.J., Agulnick,A.D., Westphal,H. and Dawid,I.B. (1998) Interactions between LIM domains and the LIM domain-binding protein Ldb1. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 4712–4717. - PubMed
-
- Carpick B.W., Graziano,V., Schneider,D., Maitra,R.K., Lee,X. and Williams,B.R.G. (1997) Characterization of the solution complex between the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase and HIV-1 trans-activating region RNA. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 9510–9516. - PubMed
-
- Cesareni G. and Murray,J.A.H. (1987) Plasmid vectors carrying the replication origin of filamentous single-stranded phages. In Setlow,J.K. and Hollaender,A. (eds), Genetic Engineering: Principles and Methods. Vol. 9. Plenum Press, New York, NY, pp. 135–154.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

