Construction, genotypic and phenotypic characterization, and immunogenicity of attenuated DeltaguaBA Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strain CVD 915
- PMID: 11447145
- PMCID: PMC98559
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.4734-4741.2001
Construction, genotypic and phenotypic characterization, and immunogenicity of attenuated DeltaguaBA Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strain CVD 915
Abstract
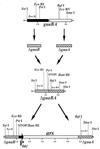
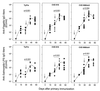
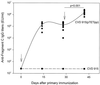
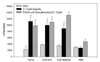
A promising live attenuated typhoid vaccine candidate strain for mucosal immunization was developed by introducing a deletion in the guaBA locus of pathogenic Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strain Ty2. The resultant DeltaguaBA mutant, serovar Typhi CVD 915, has a gene encoding resistance to arsenite replacing the deleted sequence within guaBA, thereby providing a marker to readily identify the vaccine strain. CVD 915 was compared in in vitro and in vivo assays with wild-type strain Ty2, licensed live oral typhoid vaccine strain Ty21a, or attenuated serovar Typhi vaccine strain CVD 908-htrA (harboring mutations in aroC, aroD, and htrA). CVD 915 was less invasive than CVD 908-htrA in tissue culture and was more crippled in its ability to proliferate after invasion. In mice inoculated intraperitoneally with serovar Typhi and hog gastric mucin (to estimate the relative degree of attenuation), the 50% lethal dose of CVD 915 (7.7 x 10(7) CFU) was significantly higher than that of wild-type Ty2 (1.4 x 10(2) CFU) and was only slightly lower than that of Ty21a (1.9 x 10(8) CFU). Strong serum O and H antibody responses were recorded in mice inoculated intranasally with CVD 915, which were higher than those elicited by Ty21a and similar to those stimulated by CVD 908-htrA. CVD 915 also elicited potent proliferative responses in splenocytes from immunized mice stimulated with serovar Typhi antigens. Used as a live vector, CVD 915(pTETlpp) elicited high titers of serum immunoglobulin G anti-fragment C. These encouraging preclinical data pave the way for phase 1 clinical trials with CVD 915.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel use of anaerobically induced promoter, dmsA, for controlled expression of fragment C of tetanus toxin in live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strain CVD 908-htrA.Vaccine. 2001 Feb 8;19(13-14):1694-700. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00400-x. Vaccine. 2001. PMID: 11166893
-
Safety and immune responses to attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar typhi oral live vector vaccines expressing tetanus toxin fragment C.Clin Immunol. 2000 Nov;97(2):146-53. doi: 10.1006/clim.2000.4924. Clin Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11027455
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi live vector vaccines delivered intranasally elicit regional and systemic specific CD8+ major histocompatibility class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes.Infect Immun. 2002 Aug;70(8):4009-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4009-4018.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12117906 Free PMC article.
-
CVD 908, CVD 908-htrA, and CVD 909 live oral typhoid vaccines: a logical progression.Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Jul 15;45 Suppl 1:S20-3. doi: 10.1086/518135. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17582563 Review.
-
Attenuated Salmonella as live oral vaccines against typhoid fever and as live vectors.J Biotechnol. 1996 Jan 26;44(1-3):193-6. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(95)00094-1. J Biotechnol. 1996. PMID: 8717403 Review.
Cited by
-
Recombinant Attenuated Salmonella enterica as a Delivery System of Heterologous Molecules in Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;14(17):4224. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174224. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A live Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis vaccine allows serological differentiation between vaccinated and infected animals.Infect Immun. 2007 May;75(5):2461-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01357-06. Epub 2007 Jan 29. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17261603 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between leukocytes triggers differential immune responses against Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Aug 14;13(8):e0007650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007650. eCollection 2019 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31412039 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-associated flagella enhance the protection conferred by mucosally-administered attenuated Salmonella Paratyphi A vaccines.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011 Nov;5(11):e1373. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001373. Epub 2011 Nov 1. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011. PMID: 22069504 Free PMC article.
-
Novel methods for expression of foreign antigens in live vector vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Jul;9(7):1558-64. doi: 10.4161/hv.23248. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23406777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya V I, Lowe C U, Thapa R, Gurubacharya V L, Shrestha M B, Cadoz M, Schulz D, Armand J, Bryla D A, Trollfors B, Cramton T, Schneerson R, Robbins J B. Prevention of typhoid fever in Nepal with the Vi capsular polysaccharide of Salmonella typhi. A preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:1101–1104. - PubMed
-
- Anand A C, Kataria V K, Singh W, Chatterjee S K. Epidemic multiresistant enteric fever in eastern India. Lancet. 1990;335:352–352. - PubMed
-
- Anderson R, Pasetti M F, Sztein M B, Levine M M, Noriega F R. ΔguaBA attenuated Shigella flexneri 2a strain CVD 1204 as a Shigella vaccine and as a live mucosal delivery system for fragment C of tetanus toxin. Vaccine. 2000;18:2193–2202. - PubMed
-
- Bhutta Z A, Naqvi S H, Razzaq R A, Farooqui B J. Multidrug-resistant typhoid in children: presentation and clinical features. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:832–836. - PubMed
-
- Blomfield I C, Vaughn V, Rest R F, Eisenstein B I. Allelic exchange in Escherichia coli using the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene and a temperature-sensitive pSC101 replicon. Mol Microbiol. 1991;5:1447–1457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

